Protein kinase Calpha-induced derepression of the human luteinizing hormone receptor gene transcription through ERK-mediated release of HDAC1/Sin3A repressor complex from Sp1 sites
- PMID: 18372343
- PMCID: PMC2422830
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0035
Protein kinase Calpha-induced derepression of the human luteinizing hormone receptor gene transcription through ERK-mediated release of HDAC1/Sin3A repressor complex from Sp1 sites
Abstract
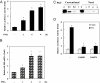
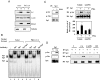
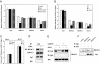
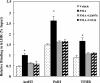
LH receptor (LHR) gene transcription is subject to repression/derepression through various modes and multiple effectors. Epigenetic silencing and activation of the LHR is achieved through coordinated regulation at both histone and DNA levels. The LHR gene is subject to repression by deacetylation and methylation at its promoter region, where a HDAC/mSin3A repressor complex is anchored at Sp1 sites. The present studies revealed that protein kinase C (PKC) alpha/ERK signaling is important for the activation of LHR promoter activity, and the increase of endogenous transcripts induced by phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA) in HeLa cells. Whereas these effects were attributable to PKCalpha activity, the ERK pathway was the downstream effector in LHR activation. PMA caused a significant enhancement of Sp1 phosphorylation at serine residue (s), which was blocked by PKCalpha or ERK inhibition. The interaction of activated phosphorylated ERK with Sp1 and ERK's association with the LHR promoter points to Sp1 as a direct target of ERK. After Sp1 phosphorylation, the HDAC1/mSin3A repressor complex dissociated from Sp1 sites, histone 3 was acetylated, and transcription factor II B and RNA polymerase II were recruited. In addition, overexpression of a constitutively active PKCalpha (PKCalpha CA) strongly activated LHR transcription in MCF-7 cells (devoid of PKCalpha), induced Sp1 phosphorylation at serine residue (s) and caused derecruitment of HDAC1/mSin3A complex from the promoter. These effects were negated by cotransfection of a dominant-negative PKCalpha. In conclusion, these studies have revealed a novel regulatory signaling mechanism of transcriptional control in which the LHR is derepressed through PKCalpha/ERK-mediated Sp1 phosphorylation, causing the release of HDAC1/mSin3A complex from the promoter.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase Czeta-induced phosphorylation of Sp1 and p107 repressor release have a critical role in histone deacetylase inhibitor-mediated derepression [corrected] of transcription of the luteinizing hormone receptor gene.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Sep;26(18):6748-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00560-06. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16943418 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of transcription of the human luteinizing hormone receptor gene by histone deacetylase-mSin3A complex.J Biol Chem. 2002 Sep 6;277(36):33431-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M204417200. Epub 2002 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12091390
-
Coordinated changes in DNA methylation and histone modifications regulate silencing/derepression of luteinizing hormone receptor gene transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Sep;25(18):7929-39. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.18.7929-7939.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16135786 Free PMC article.
-
Dual mechanisms of regulation of transcription of luteinizing hormone receptor gene by nuclear orphan receptors and histone deacetylase complexes.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003 Jun;85(2-5):401-14. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(03)00230-9. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12943729 Review.
-
Participation of signaling pathways in the derepression of luteinizing hormone receptor transcription.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010 Jan 27;314(2):221-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.05.005. Epub 2009 May 21. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19464346 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glutamine contributes to maintenance of mouse embryonic stem cell self-renewal through PKC-dependent downregulation of HDAC1 and DNMT1/3a.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(20):3292-305. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1087620. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 26375799 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic activation of mutant TERT promoter by Sp1 and GABPA in BRAFV600E-driven human cancers.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2021 Jan 22;5(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41698-020-00140-5. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33483600 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase Cdelta activation induces close homolog of adhesion molecule L1 (CHL1) expression in cultured astrocytes.Glia. 2010 Feb;58(3):315-28. doi: 10.1002/glia.20925. Glia. 2010. PMID: 19672967 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemia/reperfusion reduces transcription factor Sp1-mediated cystathionine beta-synthase expression in the kidney.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 11;285(24):18225-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.132142. Epub 2010 Apr 14. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20392694 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of transcription factor, SP1, to the promotion of HB-EGF expression in defense mechanism against the treatment of irinotecan in ovarian clear cell carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2014 Oct;3(5):1159-69. doi: 10.1002/cam4.301. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Cancer Med. 2014. PMID: 25060396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dufau ML, Tsai-Morris C-H 2007 The Leydig cell in health and disease. In: Payne AH, Hardy MP, eds. Contemporary endocrinology. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press Inc.; 227–252
-
- Dufau ML 1998 The luteinizing hormone receptor. Annu Rev Physiol 60:461–496 - PubMed
-
- Tsai-Morris C, Xie X, Wang W, Buczko E, Dufau M 1993 Promoter and regulatory regions of the rat luteinizing hormone receptor gene. J Biol Chem 268:4447–4452 - PubMed
-
- Tsai-Morris C, Geng Y, Xie X, Buczko E, Dufau M 1994 Transcriptional protein binding domains governing basal expression of the rat luteinizing hormone receptor gene. J Biol Chem 269:15868–15875 - PubMed
-
- Tsai-Morris CH, Geng Y, Buczko E, Dufau ML 1998 A novel human luteinizing hormone receptor gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:288–293 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

