Phosphorylation at serines 104 and 106 by Erk1/2 MAPK is important for estrogen receptor-alpha activity
- PMID: 18372406
- PMCID: PMC2277492
- DOI: 10.1677/JME-07-0165
Phosphorylation at serines 104 and 106 by Erk1/2 MAPK is important for estrogen receptor-alpha activity
Abstract
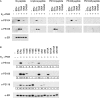
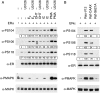
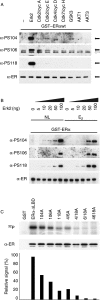
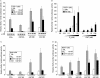
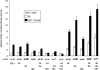
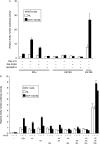
Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) at specific residues in transcription activation function 1 (AF-1) can stimulate ERalpha activity in a ligand-independent manner. This has led to the proposal that AF-1 phosphorylation and the consequent increase in ERalpha activity could contribute to resistance to endocrine therapies in breast cancer patients. Previous studies have shown that serine 118 (S118) in AF-1 is phosphorylated by extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (Erk1/2) mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in a ligand-independent manner. Here, we show that serines 104 (S104) and 106 (S106) are also phosphorylated by MAPK in vitro and upon stimulation of MAPK activity in vivo. Phosphorylation of S104 and S106 can be inhibited by the MAP-erk kinase (MEK)1/2 inhibitor U0126 and by expression of kinase-dead Raf1. Further, we show that, although S118 is important for the stimulation of ERalpha activity by the selective ER modulator 4-hydroxytamoxifen (OHT), S104 and S106 are also required for the agonist activity of OHT. Acidic amino acid substitution of S104 or S106 stimulates ERalpha activity to a greater extent than the equivalent substitution at S118, suggesting that phosphorylation at S104 and S106 is important for ERalpha activity. Collectively, these data indicate that the MAPK stimulation of ERalpha activity involves the phosphorylation not only of S118 but also of S104 and S106, and that MAPK-mediated hyperphosphorylation of ERalpha at these sites may contribute to resistance to tamoxifen in breast cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Ali S, Coombes RC. Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nature Review Cancer. 2002;2:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Arteaga CL. The epidermal growth factor receptor: from mutant oncogene in nonhuman cancers to therapeutic target in human neoplasia. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2001;19:32S–40S. - PubMed
-
- Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G. Steroid hormone receptors: many actors in search of a plot. Cell. 1995;83:851–857. - PubMed
-
- Benz CC, Scott GK, Sarup JC, Johnson RM, Tripathy D, Coronado E, Shepard HM, Osborne CK. Estrogen-dependent, tamoxifen-resistant tumorigenic growth of MCF-7 cells transfected with HER2/neu. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 1993;24:85–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

