Color constancy: phenomenal or projective?
- PMID: 18372745
- PMCID: PMC2430609
- DOI: 10.3758/pp.70.2.219
Color constancy: phenomenal or projective?
Abstract
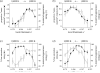
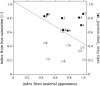
Naive observers viewed a sequence of colored Mondrian patterns, simulated on a color monitor. Each pattern was presented twice in succession, first under one daylight illuminant with a correlated color temperature of either 16,000 or 4000 K and then under the other, to test for color constancy. The observers compared the central square of the pattern across illuminants, either rating it for sameness of material appearance or sameness of hue and saturation or judging an objective property-that is, whether its change of color originated from a change in material or only from a change in illumination. Average color constancy indices were high for material appearance ratings and binary judgments of origin and low for hue-saturation ratings. Individuals' performance varied, but judgments of material and of hue and saturation remained demarcated. Observers seem able to separate phenomenal percepts from their ontological projections of mental appearance onto physical phenomena; thus, even when a chromatic change alters perceived hue and saturation, observers can reliably infer the cause, the constancy of the underlying surface spectral reflectance.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Categorical color constancy for real surfaces.J Vis. 2010 Dec 27;10(9):16. doi: 10.1167/10.9.16. J Vis. 2010. PMID: 21187350
-
Simultaneous color constancy: how surface color perception varies with the illuminant.Vision Res. 1999 Apr;39(8):1531-50. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6989(98)00192-8. Vision Res. 1999. PMID: 10343819
-
Dependence of relational colour constancy on the extraction of a transient signal.Perception. 1996;25(2):221-8. doi: 10.1068/p250221. Perception. 1996. PMID: 8733150
-
Color constancy in natural scenes with and without an explicit illuminant cue.Vis Neurosci. 2006 May-Aug;23(3-4):351-6. doi: 10.1017/S0952523806233285. Vis Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16961966
-
Immediate colour constancy.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1992 Apr;12(2):157-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-1313.1992.tb00280.x. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1992. PMID: 1408163
Cited by
-
What visual illusions tell us about underlying neural mechanisms and observer strategies for tackling the inverse problem of achromatic perception.Front Hum Neurosci. 2015 Apr 21;9:205. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00205. eCollection 2015. Front Hum Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25954181 Free PMC article.
-
Color constancy of red-green dichromats and anomalous trichromats.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Apr;51(4):2286-93. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4576. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19892868 Free PMC article.
-
The nature of instructional effects in color constancy.J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform. 2016 Jun;42(6):847-65. doi: 10.1037/xhp0000184. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform. 2016. PMID: 26727021 Free PMC article.
-
Coming to terms with lightness and brightness: effects of stimulus configuration and instructions on brightness and lightness judgments.J Vis. 2008 Aug 6;8(11):3.1-14. doi: 10.1167/8.11.3. J Vis. 2008. PMID: 18831597 Free PMC article.
-
Misidentifying illuminant changes in natural scenes due to failures in relational colour constancy.Proc Biol Sci. 2023 Nov 29;290(2011):20231676. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2023.1676. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Proc Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38018112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelson EH, Pentland AP. The perception of shading and reflectance. In: Knill DC, Richards W, editors. Perception as Bayesian Inference. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1996. pp. 409–423.
-
- Arend L, Reeves A. Simultaneous color constancy. Journal of the Optical Society of America A-Optics Image Science and Vision. 1986;3:1743–1751. - PubMed
-
- Arend LE. How much does illuminant color affect unattributed colors? Journal of the Optical Society of America A-Optics Image Science and Vision. 1993;10:2134–2147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
