The dietary histone deacetylase inhibitor sulforaphane induces human beta-defensin-2 in intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 18373608
- PMCID: PMC2561129
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02834.x
The dietary histone deacetylase inhibitor sulforaphane induces human beta-defensin-2 in intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
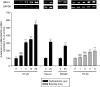
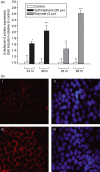
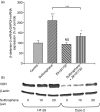
Antimicrobial peptides like human beta-defensin-2 (HBD-2) play an important role in the innate immune system protecting the intestinal mucosa against bacterial invasion. The dietary histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors sulforaphane (SFN) and butyrate have received a great deal of attention because of their ability to simultaneously modulate multiple cellular targets involved in cellular protection. In this study the influence of SFN and butyrate on HBD-2 expression as well as the molecular pathways involved in SFN-mediated induction of HBD-2 were scrutinized. Treatment of Caco-2, HT-29 and SW480 cells with SFN led to a time- and dose-dependent upregulation of HBD-2 mRNA expression as determined by semi-quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Moreover, HBD-2 protein production increased in response to SFN, measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Induction of HBD-2 was also observed in response to butyrate. Immunofluorescence analysis revealed that the protein was localized in the cytosol. Coincubation of SFN with a vitamin D receptor (VDR), or an extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2 or a nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor all reduced HBD-2 mRNA upregulation. In contrast, transfection of cells with a dominant-negative peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) mutant vector to inhibit PPARgamma wild-type action and inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling did not affect SFN-mediated upregulation of HBD-2 mRNA. Moreover, SFN induced the expression of VDR, PPARgamma and phosphorylated ERK1/2 but did not affect p38 MAPK activation. The data clearly demonstrate for the first time that the dietary HDAC inhibitor SFN is able to induce antimicrobial peptides in colonocytes. In this process HBD-2 expression is regulated via VDR, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular-regulated kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB signalling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of human beta-defensin-2 in gingival epithelial cells: the involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways, but not the NF-kappaB transcription factor family.J Immunol. 2002 Jan 1;168(1):316-24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.1.316. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11751976
-
Andrographolide exerted its antimicrobial effects by upregulation of human β-defensin-2 induced through p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathway in human lung epithelial cells.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 May;90(5):647-53. doi: 10.1139/y2012-050. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22537555
-
Defensin expression by the cornea: multiple signalling pathways mediate IL-1beta stimulation of hBD-2 expression by human corneal epithelial cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 May;44(5):1859-65. doi: 10.1167/iovs.02-0787. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 12714616 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary histone deacetylase inhibitors: from cells to mice to man.Semin Cancer Biol. 2007 Oct;17(5):363-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2007.04.001. Epub 2007 May 5. Semin Cancer Biol. 2007. PMID: 17555985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development, validation and implementation of an in vitro model for the study of metabolic and immune function in normal and inflamed human colonic epithelium.Dan Med J. 2015 Jan;62(1):B4973. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25557335 Review.
Cited by
-
Colonic MUC2 mucin regulates the expression and antimicrobial activity of β-defensin 2.Mucosal Immunol. 2015 Nov;8(6):1360-72. doi: 10.1038/mi.2015.27. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Mucosal Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25921338 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of antimicrobial host defense peptide gene expression by free fatty acids.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49558. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049558. Epub 2012 Nov 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23166711 Free PMC article.
-
The Anti-inflammatory Immune Regulation Induced by Butyrate Is Impaired in Inflamed Intestinal Mucosa from Patients with Ulcerative Colitis.Inflammation. 2020 Apr;43(2):507-517. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01133-8. Inflammation. 2020. PMID: 31797122 Free PMC article.
-
S-Layer Protein of Lactobacillus helveticus SBT2171 Promotes Human β-Defensin 2 Expression via TLR2-JNK Signaling.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 18;10:2414. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02414. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31681252 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase-mediated regulation of the antimicrobial peptide hBD2 differs in intestinal cell lines and cultured tissue.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 27;8(1):12886. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31125-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30150730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wehkamp J, Stange EF. Paneth cells and the innate immune response. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2006;22:644–50. - PubMed
-
- Sansonetti PJ. War and peace at mucosal surfaces. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:953–64. - PubMed
-
- Ganz T. Defensins: antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:710–20. - PubMed
-
- Zasloff M. Antimicrobial peptides in health and disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1199–200. - PubMed
-
- Wehkamp J, Schmid M, Fellermann K, Stange EF. Defensin deficiency, intestinal microbes, and the clinical phenotypes of Crohn's disease. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;77:460–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

