Cyclo(His-Pro) promotes cytoprotection by activating Nrf2-mediated up-regulation of antioxidant defence
- PMID: 18373731
- PMCID: PMC4496110
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00326.x
Cyclo(His-Pro) promotes cytoprotection by activating Nrf2-mediated up-regulation of antioxidant defence
Abstract
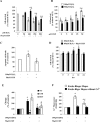
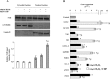
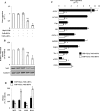
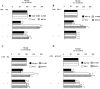
Hystidyl-proline [cyclo(His-Pro)] is an endogenous cyclic dipeptide produced by the cleavage of thyrotropin releasing hormone. Previous studies have shown that cyclo(His-Pro) protects against oxidative stress, although the underlying mechanism has remained elusive. Here, we addressed this issue and found that cyclo(His-Pro) triggered nuclear accumulation of NF-E2-related factor-2 (Nrf2), a transcription factor that up-regulates antioxidant-/electrophile-responsive element (ARE-EpRE)-related genes, in PC12 cells. Cyclo(His-Pro) attenuated reactive oxygen species production, and prevented glutathione depletion caused by glutamate, rotenone, paraquat and beta-amyloid treatment. Moreover, real-time PCR analyses revealed that cyclo(His-Pro) induced the expression of a number of ARE-related genes and protected cells against hydrogen peroxide-mediated apoptotic death. Furthermore, these effects were abolished by RNA interference-mediated Nrf2 knockdown. Finally, pharmacological inhibition of p-38 MAPK partially prevented both cyclo(His-Pro)-mediated Nrf2 activation and cellular protection. These results suggest that the signalling mechanism responsible for the cytoprotective actions of cyclo(His-Pro) would involve p-38 MAPK activation leading to Nrf2-mediated up-regulation of antioxidant cellular defence.
Figures


References
-
- Prakash KR, Tang Y, Kozikowski AP, Flippen-Anderson JL, Knoblach SM, Faden AI. Synthesis and biological activity of novel neuroprotective diketopiperazines. Bioorg Med Chem. 2002;10:3043–8. - PubMed
-
- Prasad C. Bioactive cyclic dipeptides. Peptides. 1995;16:151–64. - PubMed
-
- Jaspan JB, Banks WA, Kastin AJ. Study of passage of peptides across the blood-brain barrier: biological effects of cyclo(His-Pro) after intravenous and oral administration. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994;739:101–7. - PubMed
-
- Faden AI, Movsesyan VA, Knoblach SM, Ahmed F, Cernak I. Neuroprotective effects of novel small peptides in vitro and after brain injury. Neuropharmacology. 2005;49:410–24. - PubMed
-
- Minelli A, Bellezza I, Grottelli S, Pinnen F, Brunetti L, Vacca M. Phosphoproteomic analysis of the effect of cyclo-[His-Pro] dipeptide on PC12 cells. Peptides. 2006;27:105–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

