Sildenafil-mediated neovascularization and protection against myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury in rats: role of VEGF/angiopoietin-1
- PMID: 18373738
- PMCID: PMC3828881
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00319.x
Sildenafil-mediated neovascularization and protection against myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury in rats: role of VEGF/angiopoietin-1
Abstract
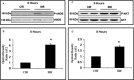
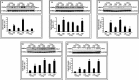
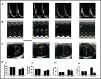
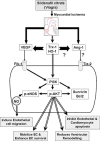
Sildenafil citrate (SC), a drug for erectile dysfunction, is now emerging as a cardiopulmonary drug. Our study aimed to determine a novel role of sildenafil on cardioprotection through stimulating angiogenesis during ischaemia (I) reperfusion (R) at both capillary and arteriolar levels and to examine the role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) in this mechanistic effect. Rats were divided into: control sham (CS), sildenafil sham (SS), control+IR (CIR) and sildenafil+IR (SIR). Rats were given 0.7 mg/kg, (i.v) of SC or saline 30 min. before occlusion of left anterior descending artery followed by reperfusion (R). Sildenafil treatment increased capillary and arteriolar density followed by increased blood flow (2-fold) compared to control. Treatment with sildenafil demonstrated increased VEGF and Ang-1 mRNA after early reperfusion. PCR data were validated by Western blot analysis. Significant reduction in infarct size, cardiomyocyte and endothelial apoptosis were observed in SC-treated rats. Increased phosphorylation of Akt, eNOS and expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, and thioredoxin, hemeoxygenase-1 were observed in SC-treated rats. Echocardiography demonstrated increased fractional shortening and ejection fraction following 45 days of reperfusion in the treatment group. Stress testing with dobutamine infusion and echocardiogram revealed increased contractile reserve in the treatment group. Our study demonstrated for the first time a strong additional therapeutic potential of sildenafil by up-regulating VEGF and Ang-1 system, probably by stimulating a cascade of events leading to neovascularization and conferring myocardial protection in in vivo I/R rat model.
Figures




References
-
- Das S, Maulik N, Das DK, Kadowitz PJ, Bivalacqua TJ. Cardioprotection with sildenafil, a selective inhibitor of cyclic 3′,5′ -monophosphate-specific phosphodi-esterase 5. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 2002;28:213–9. - PubMed
-
- Kukreja RC, Salloum F, Das A, Ockaili R, Yin C, Bremer YA, Fisher PW, Wittkamp M, Hawkins J, Chou E, Kukreja AK, Wang X, Marwaha VR, Xi L. Pharmacological preconditioning with sildenafil: basic mechanisms and clinical implications. Vascul Pharmacol. 2005;42:219–32. - PubMed
-
- Ockaili R, Salloum F, Hawkins J, Kukreja RC. Sildenafil (Viagra) induces powerful cardioprotective effect via opening of mitochondrial K(ATP) channels in rabbits. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;283:H1263–9. - PubMed
-
- Salloum F, Yin C, Xi L, Kukreja RC. Sildenafil induces delayed preconditioning through inducible nitric oxide synthase-dependent pathway in mouse heart. Circ Res. 2003;92:595–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL069910/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL056322/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL85804/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL022559/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL22559/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085804/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL56803/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL56322/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL33889/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL69910/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056322/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R29 HL056803/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056803/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

