Optimal enumeration of state space of finitely buffered stochastic molecular networks and exact computation of steady state landscape probability
- PMID: 18373871
- PMCID: PMC2375859
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-0509-2-30
Optimal enumeration of state space of finitely buffered stochastic molecular networks and exact computation of steady state landscape probability
Abstract
Background: Stochasticity plays important roles in many molecular networks when molecular concentrations are in the range of 0.1 muM to 10nM (about 100 to 10 copies in a cell). The chemical master equation provides a fundamental framework for studying these networks, and the time-varying landscape probability distribution over the full microstates, i.e., the combination of copy numbers of molecular species, provide a full characterization of the network dynamics. A complete characterization of the space of the microstates is a prerequisite for obtaining the full landscape probability distribution of a network. However, there are neither closed-form solutions nor algorithms fully describing all microstates for a given molecular network.
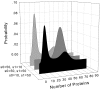
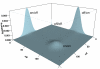
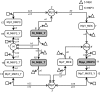
Results: We have developed an algorithm that can exhaustively enumerate the microstates of a molecular network of small copy numbers under the condition that the net gain in newly synthesized molecules is smaller than a predefined limit. We also describe a simple method for computing the exact mean or steady state landscape probability distribution over microstates. We show how the full landscape probability for the gene networks of the self-regulating gene and the toggle-switch in the steady state can be fully characterized. We also give an example using the MAPK cascade network. Data and server will be available at URL: http://scsb.sjtu.edu.cn/statespace.
Conclusion: Our algorithm works for networks of small copy numbers buffered with a finite copy number of net molecules that can be synthesized, regardless of the reaction stoichiometry, and is optimal in both storage and time complexity. The algorithm can also be used to calculate the rates of all transitions between microstates from given reactions and reaction rates. The buffer size is limited by the available memory or disk storage. Our algorithm is applicable to a class of biological networks when the copy numbers of molecules are small and the network is closed, or the network is open but the net gain in newly synthesized molecules does not exceed a predefined buffer capacity. For these networks, our method allows full stochastic characterization of the mean landscape probability distribution, and the steady state when it exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
An optimal algorithm for enumerating state space of stochastic molecular networks with small copy numbers of molecules.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007;2007:4599-602. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4353364. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007. PMID: 18003030
-
ACCURATE CHEMICAL MASTER EQUATION SOLUTION USING MULTI-FINITE BUFFERS.Multiscale Model Simul. 2016;14(2):923-963. doi: 10.1137/15M1034180. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Multiscale Model Simul. 2016. PMID: 27761104 Free PMC article.
-
Exact computation of probability landscape of stochastic networks of Single Input and Coupled Toggle Switch Modules.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;2014:5228-31. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2014.6944804. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014. PMID: 25571172 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic approaches in systems biology.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010 Jul-Aug;2(4):385-397. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.78. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20836037 Review.
-
A tutorial introduction to stochastic simulation algorithms for belief networks.Artif Intell Med. 1993 Aug;5(4):315-40. doi: 10.1016/0933-3657(93)90020-4. Artif Intell Med. 1993. PMID: 8220686 Review.
Cited by
-
Slack reactants: A state-space truncation framework to estimate quantitative behavior of the chemical master equation.J Chem Phys. 2020 Aug 7;153(5):054117. doi: 10.1063/5.0013457. J Chem Phys. 2020. PMID: 32770905 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Single-Cell Gene Pair Coexpression Landscapes by Stochastic Kinetic Modeling Reveals Gene-Pair Interactions in Development.Front Genet. 2020 Jan 31;10:1387. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01387. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32082359 Free PMC article.
-
Probabilistic control of HIV latency and transactivation by the Tat gene circuit.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 4;115(49):12453-12458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1811195115. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30455316 Free PMC article.
-
The chemical master equation approach to nonequilibrium steady-state of open biochemical systems: linear single-molecule enzyme kinetics and nonlinear biochemical reaction networks.Int J Mol Sci. 2010 Sep 20;11(9):3472-500. doi: 10.3390/ijms11093472. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20957107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network-based identification of biomarkers coexpressed with multiple pathways.Cancer Inform. 2014 Oct 16;13(Suppl 5):37-47. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S14054. eCollection 2014. Cancer Inform. 2014. PMID: 25392692 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

