Molecular genetics and racial disparities of uterine leiomyomas
- PMID: 18373954
- PMCID: PMC4171730
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2008.01.014
Molecular genetics and racial disparities of uterine leiomyomas
Abstract
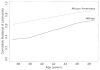
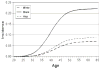
Uterine leiomyomas (ULMs) are benign oestrogen-dependent tumours of the myometrium. They are the most common tumours of the female genital tract, affecting around 77% of the female population. ULMs are more common in Black women than White women. These tumours tend to develop earlier and be more numerous, larger in size and more symptomatic in Black women than other ethnic groups. The molecular mechanism underlying this ethnic disparity is not fully understood. Polymorphism of genes involved in oestrogen synthesis and/or metabolism (COMT, CYP17), variation in the expression levels or function of oestrogen and progesterone receptors or retinoic acid nuclear receptors (retinoid acid receptor-alpha, retinoid X receptor-alpha), or aberrant expression of micro-RNAs are some of the molecular mechanisms that may be involved.
Figures
References
-
- Parker WH. Etiology, symptomatology, and diagnosis of uterine myomas. Fertil Steril. 2007;87:725–736. - PubMed
-
- Walker CL, Stewart EA. Uterine fibroids: the elephant in the room. Science. 2005;308:1589–1592. - PubMed
-
- Cramer SF, Patel A. The frequency of uterine leiomyoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990;94:435–438. - PubMed
-
- Wilcox LS, Koonin LM, Pokras R, Strauss LT, Xia Z, Peterson HB. Hysterectomy in the United States, 1988–1990. Obstet Gynecol. 1994;83:549–555. - PubMed
-
- Farquhar CM, Steiner CA. Hysterectomy rates in the United States 1990–1997. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;99:229–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous