Polymorphism of human telomeric quadruplex structures
- PMID: 18373984
- PMCID: PMC2556180
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2008.02.026
Polymorphism of human telomeric quadruplex structures
Abstract
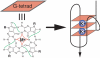
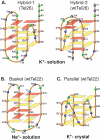
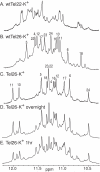
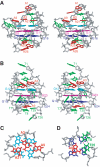
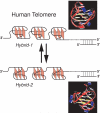
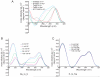
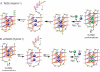
Human telomeric DNA consists of tandem repeats of the sequence d(TTAGGG). Compounds that can stabilize the intramolecular DNA G-quadruplexes formed in the human telomeric sequence have been shown to inhibit the activity of telomerase and telomere maintenance, thus the telomeric DNA G-quadruplex has been considered as an attractive target for cancer therapeutic intervention. Knowledge of intramolecular human telomeric G-quadruplex structure(s) formed under physiological conditions is important for structure-based rational drug design and thus has been the subject of intense investigation. This review will give an overview of recent progress on the intramolecular human telomeric G-quadruplex structures formed in K+ solution. It will also give insight into the structure polymorphism of human telomeric sequences and its implications for drug targeting.
Figures


References
-
- Blackburn EH. Telomere states and cell fates. Nature. 2000;408:53–56. - PubMed
-
- van Steensel B, Smogorzewska A, de Lange T. TRF2 protects human telomeres from end-to-end fusions. Cell. 1998;92:401–413. - PubMed
-
- Hackett JA, Feldser DM, Greider CW. Telomere dysfunction increases mutation rate and genomic instability. Cell. 2001;106:275–286. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn EH, Gall JG. A tandemly repeated sequence at the termini of extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. J. Mol. Biol. 1978;120:33–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

