Three-dimensional electrode displacement elastography using the Siemens C7F2 fourSight four-dimensional ultrasound transducer
- PMID: 18374467
- PMCID: PMC2597045
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.01.007
Three-dimensional electrode displacement elastography using the Siemens C7F2 fourSight four-dimensional ultrasound transducer
Abstract
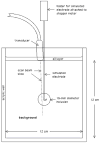
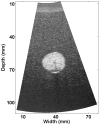
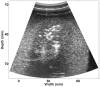
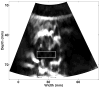
Because ablation therapy alters the elastic modulus of tissues, emerging strain imaging methods may enable clinicians for the first time to have readily available, cost-effective, real-time guidance to identify the location and boundaries of thermal lesions. Electrode displacement elastography is a method of strain imaging tailored specifically to ultrasound-guided electrode-based ablative therapies (e.g., radio-frequency ablation). Here tissue deformation is achieved by applying minute perturbations to the unconstrained end of the treatment electrode, resulting in localized motion around the end of the electrode embedded in tissue. In this article, we present a method for three-dimensional (3D) elastographic reconstruction from volumetric data acquired using the C7F2 fourSight four-dimensional ultrasound transducer, provided by Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc. (Issaquah, WA, USA). Lesion reconstruction is demonstrated for a spherical inclusion centered in a tissue-mimicking phantom, which simulates a thermal lesion embedded in a normal tissue background. Elastographic reconstruction is also performed for a thermal lesion created in vitro in canine liver using radio-frequency ablation. Postprocessing is done on the acquired raw radio-frequency data to form surface-rendered 3D elastograms of the inclusion. Elastographic volume estimates of the inclusion compare reasonably well with the actual known inclusion volume, with 3D electrode displacement elastography slightly underestimating the true inclusion volume.
Figures











References
-
- Bharat S, Madsen EL, Zagzebski JA, Varghese T. Radiofrequency Electrode Displacement Elastography - A Phantom Study. 4th International Conference on the Ultrasonic Measurement and Imaging of Tissue Elasticity; Austin, TX. 2005.
-
- Bharat S, Varghese T. Contrast-transfer improvement for electrode displacement elastography. Physics in Medicine and Biology. 2006;51:6403–6418. - PubMed
-
- Boctor E, deOliveira M, Choti M, Ghanem R, Taylor R, Hager G, Fichtinger G. Ultrasound monitoring of tissue ablation via deformation model and shape priors. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2006;9:405–412. - PubMed
-
- Fahey BJ, Nightingale KR, Stutz DL, Trahey GE. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging of thermally- and chemically-induced lesions in soft tissues: preliminary ex vivo results. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2004;30:321–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

