Chemoenzymatic synthesis of polyprenyl phosphates
- PMID: 18374576
- PMCID: PMC2471869
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.03.025
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of polyprenyl phosphates
Abstract
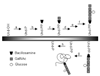
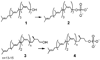
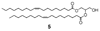
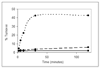
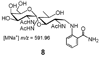
Polyprenyl phosphates, including undecaprenyl phosphate and dolichyl phosphate, are essential intermediates in several important biochemical pathways including N-linked protein glycosylation in eukaryotes and prokaryotes and prokaryotic cell wall biosynthesis. Herein, we describe the evaluation of three potential undecaprenol kinases as agents for the chemoenzymatic synthesis of polyprenyl phosphates. Target enzymes were expressed in crude cell envelope fractions and quantified via the use of luminescent lanthanide-binding tags (LBTs). The Streptococcus mutans diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) was shown to be a very useful agent for polyprenol phosphorylation using ATP as the phosphoryl transfer agent. In addition, the S. mutans DGK can be coupled with two Campylobacter jejuni glycosyltransferases involved in N-linked glycosylation to efficiently biosynthesize the undecaprenyl pyrophosphate-linked disaccharide needed for studies of PglB, the C. jejuni oligosaccharyl transferase.
Figures


References
-
- Higashi Y, Strominger JL, Sweeley CC. J. Biol. Chem. 1970;245:3697–3702. - PubMed
-
- Troy FA, Vijay IK, Tesche N. J Biol Chem. 1975;250:156–163. - PubMed
-
- Hendrickson TL, Imperiali B. Biochemistry. 1995;34:9444–9450. - PubMed
-
- Lechner J, Wieland F, Sumper M. J. Biol. Chem. 1985;260:860–866. - PubMed
-
- Szymanski CM, Wren BW. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005;3:225–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

