Stimulation of T cells up-regulates expression of Ifi202, an interferon-inducible lupus susceptibility gene, through activation of JNK/c-Jun pathway
- PMID: 18374989
- PMCID: PMC2504419
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imlet.2008.02.005
Stimulation of T cells up-regulates expression of Ifi202, an interferon-inducible lupus susceptibility gene, through activation of JNK/c-Jun pathway
Abstract
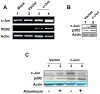
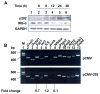
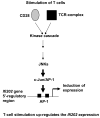
Studies have revealed that increased expression of interferon (IFN)-inducible Ifi202 gene (encoding p202 protein) in splenic B and T cells from B6.Nba2 congenic (congenic for Nb2 locus derived from NZB mice) female mice is associated with lupus susceptibility. However, signaling pathways that regulate Ifi202 expression in immune cells remain to be elucidated. Here we report that stimulation of T cells up-regulates the Ifi202 expression. We found that steady-state levels of Ifi202 mRNA and protein were detectable in splenic T cells from NZB mice and stimulation of T cells with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 up-regulated expression of the Ifi202 gene. Similarly, stimulation of cells of a mouse T cell hybridoma cell line (2B4.11) also activated transcription of the Ifi202 gene. Significantly, up-regulation of Ifi202 expression in stimulated T cells was inhibited by treatment of cells with SP600125, a specific inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Conversely, treatment of cells with anisomycin, a potent activator of the JNK and c-Jun, up-regulated Ifi202 expression. Consistent with the activation of JNK/c-Jun pathway by T cell stimulation, forced expression of c-Jun in 2B4 T cells and in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) also up-regulated the Ifi202 expression. Furthermore, we found that stimulation of T cells increased association of the activated c-Jun to the 5'-regulatory region of the Ifi202 gene in chromatin immunoprecipitation assays (ChIPs). Together, our observations demonstrate that stimulation of T cells up-regulates the Ifi202 expression in part through the JNK/c-Jun pathway.
Figures
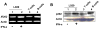
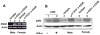
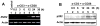



Similar articles
-
Female and male sex hormones differentially regulate expression of Ifi202, an interferon-inducible lupus susceptibility gene within the Nba2 interval.J Immunol. 2009 Dec 1;183(11):7031-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802665. Epub 2009 Nov 4. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19890043 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of mutually negative regulatory feedback loop between interferon-inducible p202 protein and the E2F family of transcription factors in lupus-prone mice.J Immunol. 2008 May 1;180(9):5927-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.9.5927. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18424712 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of Ifi202, an IFN-activatable gene, in B6.Nba2 lupus susceptible mice inhibits p53-mediated apoptosis.J Immunol. 2006 May 15;176(10):5863-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.10.5863. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16670293
-
Interferon-inducible Ifi200-family genes in systemic lupus erythematosus.Immunol Lett. 2008 Aug 15;119(1-2):32-41. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2008.06.001. Epub 2008 Jul 1. Immunol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18598717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-inducible p202 in the susceptibility to systemic lupus.Front Biosci. 2002 May 1;7:e252-62. doi: 10.2741/A921. Front Biosci. 2002. PMID: 11991834 Review.
Cited by
-
IFN-γ upregulates survivin and Ifi202 expression to induce survival and proliferation of tumor-specific T cells.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 22;5(11):e14076. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014076. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21124930 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-inducible Ifi200-family genes as modifiers of lupus susceptibility.Immunol Lett. 2012 Sep;147(1-2):10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2012.07.003. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Immunol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22841963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p204, a p200 family protein, as a multifunctional regulator of cell proliferation and differentiation.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008 Oct-Dec;19(5-6):357-69. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2008.11.002. Epub 2008 Nov 21. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008. PMID: 19027346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased expression levels of Ifi genes is associated to the increased resistance to spontaneous arthritis disease in mice deficiency of IL-1RA.BMC Immunol. 2016 Aug 2;17(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12865-016-0163-y. BMC Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27480124 Free PMC article.
-
BXSB-type genome causes murine autoimmune glomerulonephritis: pathological correlation between telomeric region of chromosome 1 and Yaa.Genes Immun. 2014 Apr-May;15(3):182-9. doi: 10.1038/gene.2014.4. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Genes Immun. 2014. PMID: 24477164
References
-
- Kotzin BL. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell. 1996;85:303–06. - PubMed
-
- Tsokos GC, Kammer GM. Molecular aberrations in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Med Today. 2000;6:418–24. - PubMed
-
- Jorgensen TN, Gubbels MR, Kotzin BL. New insights into disease pathogenesis from mouse lupus genetics. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004;16:787–93. - PubMed
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Baccala R, Beutler B, Kono DH. Type I interferons (α/β) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:307–36. - PubMed
-
- Rider V, Abdou NI. Gender differences in autoimmunity: molecular basis for estrogen effects in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Immunopharmacol. 2001;1:1009–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

