Overnight variations in cortisol, interleukin 6, tumour necrosis factor alpha and other cytokines in people with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 18375536
- PMCID: PMC2596304
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.086561
Overnight variations in cortisol, interleukin 6, tumour necrosis factor alpha and other cytokines in people with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate overnight variations in absolute values and patterns of cytokines including interleukin 6 (IL6) and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and to relate any changes to those occurring in blood cortisol.
Methods: A total of 16 people (8 female) with active RA and who had received no recent glucocorticoids were admitted overnight. Blood samples were obtained at 13 time points between 21.00 and 10.00.
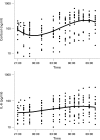
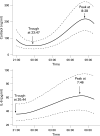
Results: The geometric mean IL6 concentration rose significantly from 35 pg/ml at 22:00 to 64 pg/ml at 07:15 (repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA), p<0.001). The geometric mean cortisol concentration rose significantly overnight from 57 ng/ml at 01:00 to 229 ng/ml at 07:15 (repeated measures ANOVA, p<0.001). Neither TNFalpha nor the other cytokines measured changed significantly. Using cubic regression modelling IL6 began to rise before cortisol (range 0.01 to 4.83 h) in eight participants and after cortisol (range 1.11 to 5.14 h) in three participants. In a random coefficient model including data from all participants, the estimated mean IL6 value began to rise 3.05 h before the estimated mean cortisol value, with the IL6 peak occurring 0.70 h before the cortisol peak.
Conclusion: The mean IL6 and cortisol concentrations showed a significant overnight variation. Neither TNFalpha nor the other cytokines measured changed significantly. In a random coefficient model IL6 began to rise approximately 3 h, and reached a peak about 40 min, before cortisol. These studies confirm that there are abnormalities in plasma cortisol and IL6 concentrations and dynamics. The data also link the overnight rise in IL6 to the circadian variation in symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circadian melatonin and cortisol levels in rheumatoid arthritis patients in winter time: a north and south Europe comparison.Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Feb;64(2):212-6. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.023416. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. PMID: 15647428 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-tumour necrosis factor antibody treatment does not change serum levels of cortisol binding globulin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis but it increases androstenedione relative to cortisol.Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Sep;64(9):1353-6. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.031997. Epub 2005 Feb 11. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. PMID: 15708882 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian relationships between interleukin (IL)-6 and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hormones: failure of IL-6 to cause sustained hypercortisolism in patients with early untreated rheumatoid arthritis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997 Apr;82(4):1279-83. doi: 10.1210/jcem.82.4.3852. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997. PMID: 9100607
-
Circadian rhythms and rheumatoid arthritis.Joint Bone Spine. 2019 May;86(3):327-333. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Joint Bone Spine. 2019. PMID: 30227223 Review.
-
Morning symptoms in rheumatoid arthritis: a defining characteristic and marker of active disease.Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 2011;125:1-5. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2011.566433. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 2011. PMID: 21529303 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of tocilizumab and tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis: a retrospective analysis of 1603 patients managed in routine clinical practice.Clin Rheumatol. 2015 Apr;34(4):673-81. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-2879-0. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Clin Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25630309 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of sunlight exposure on interleukin-6 levels in depressive and non-depressive subjects.BMC Psychiatry. 2013 Mar 5;13:75. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-75. BMC Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23497121 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the Influence of Seasonal Differences in the HPA Axis on Synchronization of the Circadian Clock and Cell Cycle.Endocrinology. 2018 Apr 1;159(4):1808-1826. doi: 10.1210/en.2017-03226. Endocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29444258 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model to Predict Disease-Mediated Therapeutic Protein-Drug Interactions: Modulation of Multiple Cytochrome P450 Enzymes by Interleukin-6.AAPS J. 2016 May;18(3):767-76. doi: 10.1208/s12248-016-9890-5. Epub 2016 Mar 9. AAPS J. 2016. PMID: 26961818 Free PMC article.
-
Stiffness is more than just duration and severity: a qualitative exploration in people with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015 Apr;54(4):615-22. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu379. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 25231178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Loubaris N, Cros G, Serrano JJ, Boucard M. Circadian and circannual variation of the carrageenin inflammatory effect in rat. Life Sci 1983;32:1349–54 - PubMed
-
- Soliman KF, Soliman MR, Owasoyo JO, Walker CA. Diurnal variation in the phlogogenic response of rats to inflammatory agents. J Pharm Pharmacol 1983;35:388–9 - PubMed
-
- Wilder RL. Neuroendocrine-immune system interactions and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol 1995;13:307–38 - PubMed
-
- Harbuz MS, Jessop DS. Is there a defect in cortisol production in rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999;38:298–302 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

