Quercetin augments TRAIL-induced apoptotic death: involvement of the ERK signal transduction pathway
- PMID: 18377872
- PMCID: PMC2430102
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.02.016
Quercetin augments TRAIL-induced apoptotic death: involvement of the ERK signal transduction pathway
Abstract
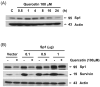
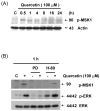
Combined treatment with quercetin and TRAIL induced cytotoxicity and enhanced annexin V staining and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage in human prostate cancer cell lines DU-145 and PC-3. These indicators of apoptosis resulted from the activation of caspase-8, -9, and -3. Although the expression levels of FLIPs, cIAP1, cIAP2, and the Bcl-2 family were not changed in quercetin-treated cells, significant downregulation of survivin occurred. Knockdown survivin by siRNA significantly increased TRAIL-induced apoptosis. We hypothesized that quercetin-induced activation of MAPK (ERK, p38, JNK) is responsible for downregulation of survivin gene expression. To test this hypothesis, we selectively inhibited MAPK during treatment with quercetin. Our data demonstrated that inhibitor of ERK (PD98059), but not p38 MAPK (SB203580) or JNK (SP600125), significantly maintained the intracellular level of survivin during treatment with quercetin. Interestingly, PD98059 also prevented quercetin-induced deacetylation of histone H3. Data from survivin promoter activity assay suggest that the Sp1 transcription factor binds to the survivin promoter region and quercetin inhibits its binding activity through deacetylation of histone H3. Quercetin-induced activation of the ERK-MSK1 signal transduction pathway may be responsible for deacetylation of histone H3. Taken together, our findings suggest that quercetin enhances TRAIL induced apoptosis by inhibition of survivin expression, through ERK-MSK1-mediated deacetylation of H3.
Figures
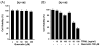
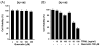
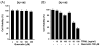






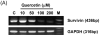
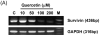




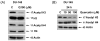
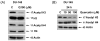
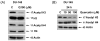


Similar articles
-
Butein sensitizes human hepatoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via extracellular signal-regulated kinase/Sp1-dependent DR5 upregulation and NF-kappaB inactivation.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Jun;9(6):1583-95. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0942. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20515942
-
Capsaicin sensitizes malignant glioma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis via DR5 upregulation and survivin downregulation.Carcinogenesis. 2010 Mar;31(3):367-75. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp298. Epub 2009 Nov 25. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 19939880
-
TRAIL apoptosis is enhanced by quercetin through Akt dephosphorylation.J Cell Biochem. 2007 Mar 1;100(4):998-1009. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21098. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17031854
-
Aspirin enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells through survivin down-regulation.Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;72(6):1586-92. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.039610. Epub 2007 Sep 11. Mol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17848598
-
Quercetin-mediated Mcl-1 and survivin downregulation restores TRAIL-induced apoptosis in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma B cells.Haematologica. 2012 Jan;97(1):38-46. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.046466. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Haematologica. 2012. PMID: 21933852 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Quercetin sensitizes fluconazole-resistant candida albicans to induce apoptotic cell death by modulating quorum sensing.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Apr;59(4):2153-68. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03599-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25645848 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis Induction in HepG2 and HCT116 Cells by a Novel Quercetin-Zinc (II) Complex: Enhanced Absorption of Quercetin and Zinc (II).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 14;24(24):17457. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417457. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139286 Free PMC article.
-
C-Phycocyanin Ameliorates Mitochondrial Fission and Fusion Dynamics in Ischemic Cardiomyocyte Damage.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jun 28;10:733. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00733. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31316386 Free PMC article.
-
Lactoferrin targeting INTL1 receptor inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression via apoptosis and cell cycle signaling pathways.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31210. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82514-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39732873 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of ERK signaling and induction of colon cancer cell death by piperlongumine.Toxicol In Vitro. 2013 Sep;27(6):1626-33. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2013.04.006. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Toxicol In Vitro. 2013. PMID: 23603476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kelley SK, Ashkenazi A. Targeting death receptors in cancer with Apo2L/TRAIL. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004;4:333–9. - PubMed
-
- Thomas LR, Henson A, Reed JC, Salsbury FR, Thorburn A. Direct binding of Fas-associated death domain (FADD) to the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor DR5 is regulated by the death effector domain of FADD. J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 30;279:32780–5. - PubMed
-
- Rowinsky EK. Targeted induction of apoptosis in cancer management: the emerging role of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor activating agents. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:9394–407. - PubMed
-
- Block G, Patterson B, Subar A. Fruit, vegetables, and cancer prevention: a review of the epidemiological evidence. Nutr Cancer. 1992;18:1–29. - PubMed
-
- Agullo G, Gamet-Payrastre L, Manenti S, Viala C, Remesy C, Chap H, Payrastre B. Relationship between flavonoid structure and inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: a comparison with tyrosine kinase and protein kinase C inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997;53:1649–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

