Amino acid starvation and colicin D treatment induce A-site mRNA cleavage in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 18377929
- PMCID: PMC2409371
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.02.065
Amino acid starvation and colicin D treatment induce A-site mRNA cleavage in Escherichia coli
Abstract
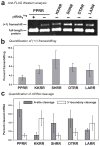
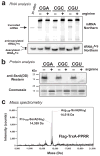
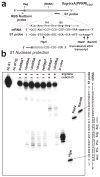
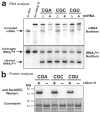
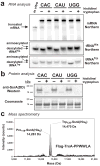
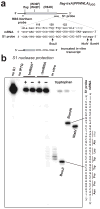
Escherichia coli possesses a unique RNase activity that cleaves stop codons in the ribosomal aminoacyl-tRNA binding site (A-site) during inefficient translation termination. This A-site mRNA cleavage allows recycling of arrested ribosomes by facilitating recruitment of the tmRNA*SmpB ribosome rescue system. To test whether A-site nuclease activity also cleaves sense codons, we induced ribosome pausing at each of the six arginine codons using three strategies; rare codon usage, arginine starvation, and inactivation of arginine tRNAs with colicin D. In each instance, ribosome pausing induced mRNA cleavage within the target arginine codons, and resulted in tmRNA-mediated SsrA-peptide tagging of the nascent polypeptide. A-site mRNA cleavage did not require the stringent factor ppGpp, or bacterial toxins such as RelE, which mediates a similar nuclease activity. However, the efficiency of A-site cleavage was modulated by the identity of the two codons immediately upstream (5' side) of the A-site codon. Starvation for histidine and tryptophan also induced A-site cleavage at histidine and tryptophan codons, respectively. Thus, A-site mRNA cleavage is a general response to ribosome pausing, capable of cleaving a variety of sense and stop codons. The induction of A-site cleavage during amino acid starvation suggests this nuclease activity may help to regulate protein synthesis during nutritional stress.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ribosomal protein S12 and aminoglycoside antibiotics modulate A-site mRNA cleavage and transfer-messenger RNA activity in Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 13;284(46):32188-200. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.062745. Epub 2009 Sep 23. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19776006 Free PMC article.
-
A-site mRNA cleavage is not required for tmRNA-mediated ssrA-peptide tagging.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 19;8(11):e81319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081319. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24260569 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavage of the A site mRNA codon during ribosome pausing provides a mechanism for translational quality control.Mol Cell. 2003 Oct;12(4):903-11. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00385-x. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 14580341
-
[A model for trans-translation].Yi Chuan. 2006 Aug;28(8):1051-4. Yi Chuan. 2006. PMID: 16870596 Review. Chinese.
-
A salvage pathway for protein structures: tmRNA and trans-translation.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003;57:101-23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090945. Epub 2003 May 1. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12730326 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequential rescue and repair of stalled and damaged ribosome by bacterial PrfH and RtcB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jul 19;119(29):e2202464119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202464119. Epub 2022 Jul 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35858322 Free PMC article.
-
A Mutant of Vibrio parahaemolyticus pirABVP (+) That Carries Binary Toxin Genes but Does Not Cause Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease.Microorganisms. 2020 Oct 8;8(10):1549. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8101549. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33049933 Free PMC article.
-
Resolving nonstop translation complexes is a matter of life or death.J Bacteriol. 2014 Jun;196(12):2123-30. doi: 10.1128/JB.01490-14. Epub 2014 Apr 4. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24706739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress response regulators identified through genome-wide transcriptome analysis of the (p)ppGpp-dependent response in Rhizobium etli.Genome Biol. 2011;12(2):R17. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-2-r17. Epub 2011 Feb 16. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 21324192 Free PMC article.
-
The tmRNA ribosome-rescue system.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2012;86:151-91. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386497-0.00005-0. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22243584 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pedersen K, Zavialov AV, Pavlov MY, Elf J, Gerdes K, Ehrenberg M. The bacterial toxin RelE displays codon-specific cleavage of mRNAs in the ribosomal A site. Cell. 2003;112:131–140. - PubMed
-
- Hayes CS, Bose B, Sauer RT. Proline residues at the C terminus of nascent chains induce SsrA tagging during translation termination. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:33825–33832. - PubMed
-
- Hayes CS, Sauer RT. Cleavage of the A site mRNA codon during ribosome pausing provides a mechanism for translational quality control. Mol Cell. 2003;12:903–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

