A thermoresponsive, microtextured substrate for cell sheet engineering with defined structural organization
- PMID: 18377979
- PMCID: PMC2673468
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.02.023
A thermoresponsive, microtextured substrate for cell sheet engineering with defined structural organization
Abstract
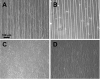
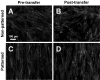
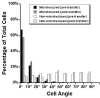
The proper function of many tissues depends critically on the structural organization of the cells and matrix of which they are comprised. Therefore, in order to engineer functional tissue equivalents that closely mimic the unique properties of native tissues it is necessary to develop strategies for reproducing the complex, highly organized structure of these tissues. To this end, we sought to develop a simple method for generating cell sheets that have defined ECM/cell organization using microtextured, thermoresponsive polystyrene substrates to guide cell organization and tissue growth. The patterns consisted of large arrays of alternating grooves and ridges (50 microm wide, 5 microm deep). Vascular smooth muscle cells cultured on these substrates produced intact sheets consisting of cells that exhibited strong alignment in the direction of the micropattern. These sheets could be readily transferred from patterned substrates to non-patterned substrates without the loss of tissue organization. Ultimately, such sheets will be layered to form larger tissues with defined ECM/cell organization that spans multiple length scales.
Figures
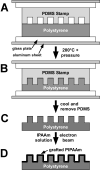
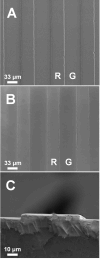
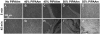
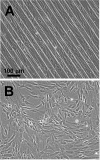
References
-
- Fung YC. Biomechanics: Mechanical Properties of Living Tissues. New York: Spinger-Verlag; 1993.
-
- Isenberg BC, Williams C, Tranquillo RT. Small-diameter artificial arteries engineered in vitro. Circ Res. 2006;98(1):25–35. - PubMed
-
- Teebken OE, Haverich A. Tissue engineering of small diameter vascular grafts. Eur J of Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2002;23(6):475–485. - PubMed
-
- Schmedlen RH, Elbjeirami WM, Gobin AS, West JL. Tissue engineered small-diameter vascular grafts. Clin Plast Surg. 2003;30(4):507–517. - PubMed
-
- Canham PB, Talman EA, Finlay HM, Dixon JG. Medial collagen organization in human arteries of the heart and brain by polarized light microscopy. Connect Tissue Res. 1991;26(12):121–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

