Imaging the spread of reversible brain inactivations using fluorescent muscimol
- PMID: 18377997
- PMCID: PMC2440580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.01.033
Imaging the spread of reversible brain inactivations using fluorescent muscimol
Abstract
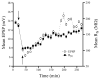
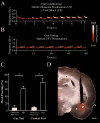
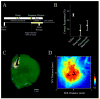
Muscimol is a GABA A-agonist that causes rapid and reversible suppression of neurophysiological activity. Interpretations of the effects of muscimol infusions into the brain have been limited because of uncertainty about spread of the drug around the injection site. To solve this problem, the present study explored the use of a fluorophore-conjugated muscimol molecule (FCM). Whole-cell recordings from horizontal brain slices demonstrated that bath-applied FCM acts like muscimol in reversibly suppressing excitatory synaptic transmission. Two types of in vivo experiments demonstrated that the behavioral effects of FCM infusion are similar to the behavioral effects of muscimol infusion. FCM infusion into the rat amygdala before fear conditioning impaired both cued and contextual freezing, which were tested 24 or 48 h later. Normal fear conditioning occurred when these same rats were subsequently given phosphate-buffered saline infusions. FCM infusion into the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex impaired accuracy during a delayed-response task. Histological analysis showed that the region of fluorescence was restricted to 0.5-1mm from the injection site. Myelinated fiber tracts acted as diffusional barriers, thereby shaping the overall spread of fluorescence. The results suggest that FCM is indeed useful for exploring the function of small brain regions.
Figures
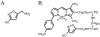

References
-
- Arikan R, Blake NMJ, Erinjeri JP, Woolsey TA, Giraud L, Highstein SM. A method to measure the effective spread of focally injected muscimol into the central nervous system with electrophysiology and light microscopy J. Neurosci Methods. 2002;118:51–57. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JW. The production of ultrasonic sounds by laboratory rats and other mammals. Science. 1954;19:808–809. - PubMed
-
- Beaumont K, Chilton WS, Yamamura HI, Enna SJ. Muscimol binding in rat brain: Association with synaptic GABA receptors. Brain Res. 1978;148:153–162. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC. Crouching as an index of fear. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1969;67:370–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

