Solvent-free matrix dry-coating for MALDI imaging of phospholipids
- PMID: 18378160
- PMCID: PMC2696184
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jasms.2008.02.013
Solvent-free matrix dry-coating for MALDI imaging of phospholipids
Abstract
A fast and simple, solvent-free matrix deposition protocol was developed for positive ionization mode phospholipid analysis in tissues. Finely ground 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid was deposited onto sagittal mouse brain sections using a dry-coating technique, in which solid matrix particles were filtered directly onto the tissue through a 20-microm stainless steel sieve. Phospholipid signals were obtained directly off these sections, allowing acquisition of high-resolution MS images. These images were compared to those from serial sections that were spray-coated with a thin-layer chromatography (TLC) reagent sprayer. Signals obtained from the dry matrix deposition method were comparable to those from spray-coated sections, producing identical localization patterns with a simpler and faster sample preparation with virtually no analyte delocalization. This approach was found to yield highly reproducible results, eliminating much of the variance caused by operator differences, and making it an attractive alternative to the currently used matrix application methods.
Figures

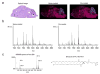

References
-
- Caprioli RM, Farmer TB, Gile J. Molecular imaging of biological samples: localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal Chem. 1997;69:4751. - PubMed
-
- Chaurand P, Caprioli RM. Direct profiling and imaging of peptides and proteins from mammalian cells and tissue sections by mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis. 2002;23:3125. - PubMed
-
- Chaurand P, Schwartz SA, Caprioli RM. Profiling and imaging proteins in tissue sections by mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2004;76:86A. - PubMed
-
- Mills GB, Moolenaar WH. The emerging role of lysophosphatidic acid in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2003;8:582. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura S, Nishizuka Y. Lipid mediators and protein kinase C activation for the intracellular signaling network. J Biochem. 1994;115:1029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

