Inhibition of hepatitis B virus gene expression and replication by endoribonuclease-prepared siRNA
- PMID: 18378325
- PMCID: PMC7112819
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2008.02.008
Inhibition of hepatitis B virus gene expression and replication by endoribonuclease-prepared siRNA
Abstract
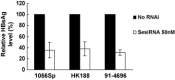
Endoribonuclease-prepared siRNA (esiRNA) is an alternative tool to chemical synthetic siRNA for gene silencing. Since esiRNAs are directed against long target sequences, the genetic variations in the target sequences will have little influence on their effectiveness. The ability of esiRNAs to inhibit hepatitis B virus (HBV) gene expression and replication was tested. EsiRNAs targeting the coding region of HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) and the nucleocapsid (HBcAg) inhibited specifically the expression of HBsAg and HBcAg when cotransfected with the respective expression plasmids. Both esiRNAs reduced the HBV transcripts and replication intermediates in transient transfected cells and cells with HBV genomes integrated stably. Compared with synthetic siRNA, esiRNA targeting HBsAg was less effective than the selected synthetic siRNA in terms of the inhibition of HBV gene expression and replication. However, while the ability of synthetic siRNAs for specific gene silencing was impaired strongly by the nucleotide substitutions within the target sequences. The efficiency of gene silencing by esiRNAs was not influenced by sequence variation. The transfection of esiRNA did not induce interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) like STAT1 and ISG15, indicating the absence of off-target effects. In general, esiRNAs strongly inhibited HBV gene expression and replication and may have an advantage against HBV strains which are variable genetically.
Figures





Similar articles
-
RNA interference against hepatitis B virus with endoribonuclease-prepared siRNA despite of the target sequence variations.Virus Res. 2007 Jun;126(1-2):172-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.02.013. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Virus Res. 2007. PMID: 17399837
-
siRNA pool targeting different sites of human hepatitis B surface antigen efficiently inhibits HBV infection.J Drug Target. 2008 Feb;16(2):140-8. doi: 10.1080/10611860701878750. J Drug Target. 2008. PMID: 18274934 Free PMC article.
-
EsiRNAs inhibit Hepatitis B virus replication in mice model more efficiently than synthesized siRNAs.Virus Res. 2006 Jun;118(1-2):150-5. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.12.005. Epub 2006 Jan 19. Virus Res. 2006. PMID: 16423421
-
Exploiting the RNA interference pathway to counter hepatitis B virus replication.Liver Int. 2005 Feb;25(1):9-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2004.0966.x. Liver Int. 2005. PMID: 15698393 Review.
-
Model-based meta-analysis to quantify the effects of short interfering RNA therapeutics on hepatitis B surface antigen turnover in hepatitis B-infected mice.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024 May;13(5):729-742. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13129. Epub 2024 Mar 24. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38522000 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of the blood-testis barrier by coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Oct 15;303(8):C843-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00218.2012. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22875787 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulated phospholipid synthesis is key for hepatitis B virus replications.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 10;9(1):12989. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49367-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31506451 Free PMC article.
-
The dose of HBV genome contained plasmid has a great impact on HBV persistence in hydrodynamic injection mouse model.Virol J. 2017 Oct 25;14(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0874-6. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 29070073 Free PMC article.
-
Polarity protein Crumbs homolog-3 (CRB3) regulates ectoplasmic specialization dynamics through its action on F-actin organization in Sertoli cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 30;6:28589. doi: 10.1038/srep28589. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27358069 Free PMC article.
-
An efficient antiviral strategy for targeting hepatitis B virus genome using transcription activator-like effector nucleases.Mol Ther. 2014 Feb;22(2):303-311. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.212. Epub 2013 Sep 12. Mol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24025750 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aigner A. Gene silencing through RNA interference (RNAi) in vivo: strategies based on the direct application of siRNAs. J. Biotechnol. 2006;124(1):12–25. - PubMed
-
- Giladi H., Ketzinel-Gilad M., Rivkin L., Felig Y., Nussbaum O., Galun E. Small interfering RNA inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in mice. Mol. Ther. 2003;8:769–776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

