Phase II study of dose-adjusted EPOCH and rituximab in untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with analysis of germinal center and post-germinal center biomarkers
- PMID: 18378569
- PMCID: PMC2409217
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.1391
Phase II study of dose-adjusted EPOCH and rituximab in untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with analysis of germinal center and post-germinal center biomarkers
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the clinical outcome and the influence of biomarkers associated with apoptosis inhibition (Bcl-2), tumor proliferation (MIB-1), and cellular differentiation on the outcome with dose-adjusted (DA) EPOCH (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin) plus rituximab (R) infusional therapy in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) with analysis of germinal center B-cell (GCB) and post-GCB subtypes by immunohistochemistry.
Patients and methods: Phase II study of 72 patients with untreated de novo DLBCL who were at least 18 years of age and stage II or higher. Radiation consolidation was not permitted.
Results: Patients had a median age of 50 years (range, 19 to 85) and 40% had a high-intermediate or high International Prognostic Index (IPI). At 5 years, progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 79% and 80%, respectively, with a median potential follow-up of 54 months. PFS was 91%, 90%, 67%, and 47%, and OS was 100%, 90%, 74%, and 37%, for 0 to 1, 2, 3, and 4 to 5 IPI factors, respectively, at 5 years. The Bcl-2 and MIB-1 biomarkers were not associated with PFS or OS. Based on DA-EPOCH historical controls, rituximab only benefited Bcl-2 positive tumors. Bcl-6 expression was associated with higher PFS whereas GCB exhibited a marginally significant higher PFS compared with post-GCB DLBCL.
Conclusion: DA-EPOCH-R outcome was not affected by tumor proliferation and rituximab appeared to overcome the adverse effect of Bcl-2. Bcl-6 may identify a biologic program associated with a superior outcome. Overall, DA-EPOCH-R shows promising outcome in low and intermediate IPI groups. A molecular model of treatment outcome with rituximab and chemotherapy is presented.
Figures
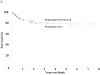


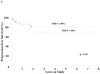





 of rituximab, and CHOP and DA-EPOCH with and without rituximab along the continuum from germinal center to post-germinal center DLBCL are shown. Rituximab benefit is primarily in post-GCB DLBCL where it modulates drug resistance and “equalizes” differences among chemotherapy regimens. In GCB DLBCL, DA-EPOCH-R may show an advantage in part due to extended delivery of topoisomerase II agents.
of rituximab, and CHOP and DA-EPOCH with and without rituximab along the continuum from germinal center to post-germinal center DLBCL are shown. Rituximab benefit is primarily in post-GCB DLBCL where it modulates drug resistance and “equalizes” differences among chemotherapy regimens. In GCB DLBCL, DA-EPOCH-R may show an advantage in part due to extended delivery of topoisomerase II agents.References
-
- Fisher RI, Gaynor ER, Dahlberg S, et al. Comparison of a standard regimen (CHOP) with three intensive chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1002–6. - PubMed
-
- Wilson WH. Drug resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Semin Hematol. 2006;43:230–9. - PubMed
-
- Wilson WH, Teruya-Feldstein J, Fest T, et al. Relationship of p53, bcl-2, and tumor proliferation to clinical drug resistance in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Blood. 1997;89:601–9. - PubMed
-
- Miller TP, Grogan TM, Dahlberg S, et al. Prognostic significance of the Ki-67-associated proliferative antigen in aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas: a prospective Southwest Oncology Group trial. Blood. 1994;83:1460–6. - PubMed
-
- Moskowitz C, Hamlin PA, Horwitz SM, et al. Phase II Trial of Dose-Dense R-CHOP Followed by Risk-Adapted Consolidation with Either ICE or ICE and ASCT, Based upon the Results of Biopsy Confirmed Abnormal Interim Restaging PET Scan, Improves Outcome in Patients with Advanced Stage DLBCL. ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts. 2006;108:532.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

