Involvement of OA1, an intracellular GPCR, and G alpha i3, its binding protein, in melanosomal biogenesis and optic pathway formation
- PMID: 18378571
- PMCID: PMC2881626
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.08-1806
Involvement of OA1, an intracellular GPCR, and G alpha i3, its binding protein, in melanosomal biogenesis and optic pathway formation
Abstract
Purpose: Ocular albinism type 1 (OA1) is characterized by abnormalities in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) melanosomes and misrouting of optic axons. The OA1 gene encodes a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that coimmunoprecipitates with the G alpha i-subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins from human melanocyte extracts. This study was undertaken to test whether one of the G alpha i proteins, G alpha i3, signals in the same pathway as OA1 to regulate melanosome biogenesis and axonal growth through the optic chiasm.
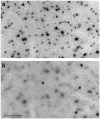
Methods: Adult G alpha i3(-/-) and Oa1(-/-) mice were compared with their respective control mice (129Sv and B6/NCrl) to study the effects of the loss of G alpha i3 or Oa1 function. Light and electron microscopy were used to analyze the morphology of the retina and the size and density of RPE melanosomes, electroretinograms to study retinal function, and retrograde labeling to investigate the size of the uncrossed optic pathway.
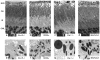
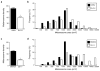
Results: Although G alpha i3(-/-) and Oa1(-/-) photoreceptors were comparable to those of the corresponding control retinas, the density of their RPE melanosomes was significantly lower than in control RPEs. In addition, the RPE cells of G alpha i3(-/-) and Oa1(-/-) mice showed abnormal melanosomes that were far larger than the largest 129Sv and B6/NCrl melanosomes, respectively. Although G alpha i3(-/-) and Oa1(-/-) mice had normal results on electroretinography, retrograde labeling showed a significant reduction from control in the size of their ipsilateral retinofugal projections.
Conclusions: These results indicate that G alpha i3, like Oa1, plays an important role in melanosome biogenesis. Furthermore, they suggest a common Oa1-G alpha i3 signaling pathway that ultimately affects axonal growth through the optic chiasm.
Figures
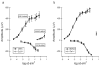
Similar articles
-
Specific interaction of Gαi3 with the Oa1 G-protein coupled receptor controls the size and density of melanosomes in retinal pigment epithelium.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024376. Epub 2011 Sep 8. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21931697 Free PMC article.
-
A constitutively active Gαi3 protein corrects the abnormal retinal pigment epithelium phenotype of Oa1-/- mice.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 30;8(9):e76240. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076240. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24098784 Free PMC article.
-
Oa1 knock-out: new insights on the pathogenesis of ocular albinism type 1.Hum Mol Genet. 2000 Nov 22;9(19):2781-8. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.19.2781. Hum Mol Genet. 2000. PMID: 11092754
-
The ocular albinism type 1 (OA1) protein and the evidence for an intracellular signal transduction system involved in melanosome biogenesis.Pigment Cell Res. 2005 Aug;18(4):227-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.2005.00240.x. Pigment Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 16029416 Review.
-
Signaling pathways in melanosome biogenesis and pathology.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;42(7):1094-104. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.03.023. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20381640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Macular optical coherence tomography findings and GPR143 mutations in patients with ocular albinism.Int Ophthalmol. 2014 Oct;34(5):1075-81. doi: 10.1007/s10792-014-9912-1. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Int Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24526317
-
Simultaneous Expression of ABCA4 and GPR143 Mutations: A Complex Phenotypic Manifestation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Jun 1;57(7):3409-15. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-19621. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27367509 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular Albinism Type 1 Regulates Deltamethrin Tolerance in Lymantria dispar and Drosophila melanogaster.Front Physiol. 2019 Jun 19;10:766. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00766. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31275171 Free PMC article.
-
GNAI3: Another Candidate Gene to Screen in Persons with Ocular Albinism.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 8;11(9):e0162273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162273. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27607449 Free PMC article.
-
Polarized Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium Exhibits Distinct Surface Proteome on Apical and Basal Plasma Membranes.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1722:223-247. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7553-2_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29264809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schiaffino MV, Bassi MT, Galli L, et al. Analysis of the OA1 gene reveals mutations in only one-third of patients with X-linked ocular albinism. Hum Mol Genet. 1995;4(12):2319–2325. - PubMed
-
- King RA, Mentink MM, Oetting WS. Albinism. In: Svriver CR, Beaudet A, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1995. pp. 4353–4392.
-
- Newton JM, Orlow ST, Barsh GS. Isolation and characterization of the mouse homolog of the X linked ocular albinism (OA1) gene. Genomics. 1996;37(2):219–225. - PubMed
-
- Incerti B, Cortese K, Pizzigoni A, et al. OA1 knockout: new insights on the pathogenesis of ocular albinism type 1. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:2781–2788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

