Complementary roles for biomarkers of biomechanical strain ST2 and N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction
- PMID: 18378613
- PMCID: PMC4273564
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.728022
Complementary roles for biomarkers of biomechanical strain ST2 and N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: ST2 is a member of the interleukin-1 receptor family with a soluble form that is markedly upregulated on application of biomechanical strain to cardiac myocytes. Circulating ST2 levels are elevated in the setting of acute myocardial infarction, but the predictive value of ST2 independent of traditional clinical factors and of an established biomarker of biomechanical strain, N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), has not been established.
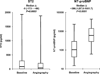
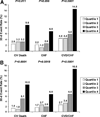
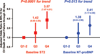
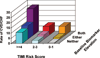
Methods and results: We measured ST2 at baseline in 1239 patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction from the CLopidogrel as Adjunctive ReperfusIon TherapY-Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction 28 (CLARITY-TIMI 28) trial. Per trial protocol, patients were to undergo coronary angiography after 2 to 8 days and were followed up for 30 days for clinical events. In contrast to NT-proBNP, ST2 levels were independent of clinical factors potentially related to chronic increased left ventricular wall stress, including age, hypertension, prior myocardial infarction, and prior heart failure; levels also were only modestly correlated with NT-proBNP (r=0.14). After adjustment for baseline characteristics and NT-proBNP levels, an ST2 level above the median was associated with a significantly greater risk of cardiovascular death or heart failure (third quartile: adjusted odds ratio, 1.42; 95% confidence interval, 0.68 to 3.57; fourth quartile: adjusted odds ratio, 3.57; 95% confidence interval, 1.87 to 6.81; P<0.0001 for trend). When both ST2 and NT-proBNP were added to a model containing traditional clinical predictors, the c statistic significantly improved from 0.82 (95% confidence interval, 0.77 to 0.87) to 0.86 (95% confidence interval, 0.81 to 0.90) (P=0.017).
Conclusions: In ST-elevation myocardial infarction, high baseline ST2 levels are a significant predictor of cardiovascular death and heart failure independently of baseline characteristics and NT-proBNP, and the combination of ST2 and NT-proBNP significantly improves risk stratification. These data highlight the prognostic value of multiple, complementary biomarkers of biomechanical strain in ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures

References
-
- Wagner GS, Roe CR, Limbird LE, Rosati RA, Wallace AG. The importance of identification of the myocardial-specific isoenzyme of creatine phosphokinase (MB form) in the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1973;47:263–269. - PubMed
-
- Hamm CW, Ravkilde J, Gerhardt W, Jorgensen P, Peheim E, Ljungdahl L, Goldmann B, Katus HA. The prognostic value of serum troponin T in unstable angina. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:146–150. - PubMed
-
- Antman EM, Tanasijevic MJ, Thompson B, Schactman M, McCabe CH, Cannon CP, Fischer GA, Fung AY, Thompson C, Wybenga D, Braunwald E. Cardiac-specific troponin I levels to predict the risk of mortality in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1342–1349. - PubMed
-
- O’Donoghue M, de Lemos JA, Morrow DA, Murphy SA, Buros JL, Cannon CP, Sabatine MS. Prognostic utility of heart-type fatty acid binding protein in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2006;114:550–557. - PubMed
-
- de Lemos JA, Morrow DA, Bentley JH, Omland T, Sabatine MS, McCabe CH, Hall C, Cannon CP, Braunwald E. The prognostic value of B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1014–1021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

