Coenzyme F420-dependent sulfite reductase-enabled sulfite detoxification and use of sulfite as a sole sulfur source by Methanococcus maripaludis
- PMID: 18378657
- PMCID: PMC2423035
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00098-08
Coenzyme F420-dependent sulfite reductase-enabled sulfite detoxification and use of sulfite as a sole sulfur source by Methanococcus maripaludis
Abstract
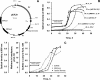
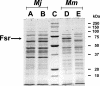
Coenzyme F(420)-dependent sulfite reductase (Fsr) of Methanocaldococcus jannaschii, a sulfite-tolerant methanogen, was expressed with activity in Methanococcus maripaludis, a sulfite-sensitive methanogen. The recombinant organism reduced sulfite to sulfide and grew with sulfite as the sole sulfur source, indicating that Fsr is a sulfite detoxification and assimilation enzyme for methanogens and that M. maripaludis synthesizes siroheme.
Figures

References
-
- Baumer, S., T. Ide, C. Jacobi, A. Johann, G. Gottschalk, and U. Deppenmeier. 2000. The F420H2 dehydrogenase from Methanosarcina mazei is a redox-driven proton pump closely related to NADH dehydrogenases. J. Biol. Chem. 275:17968-17973. - PubMed
-
- Becker, D. F., and S. W. Ragsdale. 1998. Activation of methyl-SCoM reductase to high specific activity after treatment of whole cells with sodium sulfide. Biochemistry 37:2639-2647. - PubMed
-
- Boone, D. R., W. B. Whitman, and P. Rouviére. 1993. Microbiology, diversity and taxonomy of methanogens, p. 35-80. In J. G. Ferry (ed.), Methanogenesis: ecology, physiology, biochemistry and genetics. Chapman and Hall, New York, NY.
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

