Delayed development of linezolid resistance in Staphylococcus aureus following exposure to low levels of antimicrobial agents
- PMID: 18378719
- PMCID: PMC2415777
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01302-07
Delayed development of linezolid resistance in Staphylococcus aureus following exposure to low levels of antimicrobial agents
Abstract
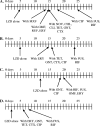
The development of resistance to linezolid (LZD) in gram-positive bacteria depends on the mutation of a single 23S rRNA gene, followed by homologous recombination and gene conversion of the other alleles. We sought to inhibit this process in Staphylococcus aureus using a range of antibacterial agents, including some that suppress recombination. A model for the rapid selection of LZD resistance was developed which allowed the selection of LZD-resistant mutants with G2576T mutations in all five copies of the 23S rRNA gene following only 5 days of subculture. The emergence of LZD-resistant isolates was delayed by exposing cultures to low concentrations of various classes of antibiotics. All antibiotic classes were effective in delaying the selection of LZD-resistant mutants and, with the exception of fusidic acid (FUS) and rifampin (RIF), prolonged the selection window from 5 to approximately 15 days. Inhibitors of DNA processing were no more effective than any other class of antibiotics at suppressing resistance development. However, the unrelated antimicrobials FUS and RIF were particularly effective at preventing the emergence of LZD resistance, prolonging the selection window from 5 to 25 days. The enhanced suppressive effect of FUS and RIF on the development of LZD resistance was lost in a recA-deficient host, suggesting that these drugs affect recA-dependent recombination. Furthermore, FUS and RIF were shown to be effective inhibitors of homologous recombination of a plasmid into the staphylococcal chromosome. We suggest that RIF or FUS in combination with LZD may have a role in preventing the emergence of LZD resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Bayles, K. W., E. W. Brunskill, J. J. Iandolo, L. L. Hruska, S. Huang, P. A. Pattee, B. K. Smiley, and R. E. Yasbin. 1994. A genetic and molecular characterization of the recA gene from Staphylococcus aureus. Gene 147:13-20. - PubMed
-
- BSAC. 1991. A guide to sensitivity testing; report of the working party on antibiotic sensitivity testing of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 27(Suppl. D):1-50. - PubMed
-
- Chambers, H. F. 1999. Penicillin-binding protein-mediated resistance in pneumococci and staphylococci. J. Infect. Dis. 179:S353-S359. - PubMed
-
- Chopra, I., A. J. O'Neill, and K. Miller. 2003. The role of mutators in the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Drug Resist. Updat. 6:137-145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

