Increase in reactive oxygen species and activation of Akt signaling pathway in neuropathic pain
- PMID: 18379870
- PMCID: PMC11515024
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-008-9279-9
Increase in reactive oxygen species and activation of Akt signaling pathway in neuropathic pain
Abstract
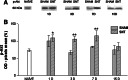
Neuropathic pain occurs as a result of peripheral or central nervous system injury. Its pathophysiology involves mainly a central sensitization mechanism that may be correlated to many molecules acting in regions involved in pain processing, such as the spinal cord. It has been demonstrated that reactive oxygen species (ROS) and signaling molecules, such as the serine/threonine protein kinase Akt, are involved in neuropathic pain mechanisms. Thus, the aim of this study was to provide evidence of this relationship. Sciatic nerve transection (SNT) was used to induce neuropathic pain in rats. Western blot analysis of Akt and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE)-Michael adducts, and measurement of hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) in the lumbosacral spinal cord were performed. The main findings were found seven days after SNT, when there was an increase in HNE-Michael adducts formation, total and p-Akt expression, and H(2)O(2) concentration. However, one and 15 days after SNT, H(2)O(2) concentration was raised in both sham (animals that were submitted to surgery without nerve injury) and SNT groups, showing the high sensibility of this ROS to nociceptive afferent stimuli, not only to neuropathic pain. p-Akt also increased in sham and SNT groups one day post injury, but at 3 and 7 days the increase occurred exclusively in SNT animals. Thus, there is crosstalk between intracellular signaling pathways and ROS, and these molecules can act as protective agents in acute pain situations or play a role in the development of chronic pain states.
Figures



References
-
- Alessi DR, Cohen P (1998) Mechanism of activation and function of protein kinase B. Curr Opin Genet Dev 8(1):55–62 - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254 - PubMed
-
- Chao MV, Rajagopal R, Lee FS (2006) Neurotrophin signalling in health and disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 110(2):167–173 - PubMed
-
- Chizh BA, Gohring M, Troster A, Quartey GK, Schmelz M, and Koppert W (2007) Effects of oral pregabalin and aprepitant on pain and central sensitization in the electrical hyperalgesia model in human volunteers. Br J Anaesth 98(2):246–254 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

