Endothelin-1 reduces p-glycoprotein transport activity in an in vitro model of human adult blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 18379872
- PMCID: PMC11515797
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-008-9277-y
Endothelin-1 reduces p-glycoprotein transport activity in an in vitro model of human adult blood-brain barrier
Abstract
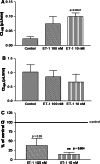
Aims: It is a huge challenge to understand the blood-brain barrier (BBB), which is a key element in neuroinflammation associated with many brain diseases. The BBB also regulates the passage of xenobiotics into the central nervous system (CNS), and therefore influences drug efficacy. This may be due to the presence of ATP binding cassette transporters such as P-glycoprotein (Pgp) on the BBB, which are efflux pumps known to transport many drugs. The peptide endothelin 1 (ET-1) is involved in different kinds of CNS diseases and neuroinflammation, and is known to modulate Pgp transport activity. Although there are data from animal models, data from human models are scarce. We evaluated Pgp expression and transport activity in adult human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) when exposing an adult human in vitro BBB model to ET-1.
Methods: Adult HBMECs were cocultured with human adult glial cells on a Transwells to mimic blood and CNS compartments. These human in vitro BBBs were exposed for 24 h to 100 nM and 10 nM ET-1. Pgp expression was assessed by flow cytometry and its transport activity by measuring radiolabelled digoxin passage.
Results: After exposure to ET-1, flow cytometry showed no shift of fluorescence intensity for a Pgp specific antibody. The passage of digoxin increased with a significant decrease of Q ratio for 10 nM ET-1.
Conclusion: Our results show that ET-1 has no effect on Pgp expression of adult HBMECs, but does modulate Pgp transport activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Susceptibility of juvenile and adult blood-brain barrier to endothelin-1: regulation of P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein expression and transport activity.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Dec 19;9:273. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-273. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 23253775 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in P-glycoprotein activity in human and rodent blood-brain barrier assessed by mechanistic modelling.Arch Toxicol. 2021 Sep;95(9):3015-3029. doi: 10.1007/s00204-021-03115-y. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Arch Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34268580 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-induced trafficking of p-glycoprotein in human brain capillary endothelial cells as demonstrated by exposure to mitomycin C.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 4;9(2):e88154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088154. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24505408 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Regulation Mechanisms of P-gp in the Blood-Brain Barrier in Hypoxia.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(10):1041-1051. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190610140153. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31187705 Review.
-
P-glycoprotein trafficking as a therapeutic target to optimize CNS drug delivery.Adv Pharmacol. 2014;71:25-44. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Adv Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25307213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The multidrug resistance 1 gene Abcb1 in brain and placenta: comparative analysis in human and guinea pig.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 29;9(10):e111135. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111135. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25353162 Free PMC article.
-
Drug transport into the central nervous system: using newer findings about the blood-brain barriers.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2012 Jun;2(3):152-9. doi: 10.1007/s13346-012-0058-2. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 25786864
-
The role of reactive oxygen species in the regulation of the blood-brain barrier.Tissue Barriers. 2025;13(2):2361202. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2024.2361202. Epub 2024 May 29. Tissue Barriers. 2025. PMID: 38808582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipopolysaccharide impairs blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein function in mice through prostaglandin- and nitric oxide-independent pathways.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;4(2):276-82. doi: 10.1007/s11481-008-9138-y. Epub 2008 Nov 28. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19039663 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive procedures reduce perihematomal endothelin-1 levels and the permeability of the BBB in a rabbit model of intracerebral hematoma.Neurol Sci. 2013 Jan;34(1):41-9. doi: 10.1007/s10072-012-0962-8. Epub 2012 Feb 5. Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 22311641
References
-
- Arai H, Hori S, Aramori I, Ohkubo H, Nakanishi S (1990) Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature 348:730–732 - PubMed
-
- Bagnato A, Rosano L, Spinella F, Di Castro V, Tecce R, Natali PG (2004) Endothelin B receptor blockade inhibits dynamics of cell interactions and communications in melanoma cell progression. Cancer Res 64:1436–1443 - PubMed
-
- Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M (2004) The blood-brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis 16:1–13 - PubMed
-
- Barone FC, Willette RN, Yue TL, Feurestein G (1995) Therapeutic effects of endothelin receptor antagonists in stroke. Neurol Res 17:259–264 - PubMed
-
- Bauer B, Hartz AM, Miller DS (2007) Tumor necrosis factor alpha and endothelin-1 increase P-glycoprotein expression and transport activity at the blood-brain barrier. Mol Pharmacol 71:667–675 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

