Danaparoid sodium inhibits systemic inflammation and prevents endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats
- PMID: 18380908
- PMCID: PMC2447588
- DOI: 10.1186/cc6851
Danaparoid sodium inhibits systemic inflammation and prevents endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats
Abstract
Introduction: Systemic inflammatory mediators, including high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), play an important role in the development of sepsis. Anticoagulants, such as danaparoid sodium (DA), may be able to inhibit sepsis-induced inflammation, but the mechanism of action is not well understood. We hypothesised that DA would act as an inhibitor of systemic inflammation and prevent endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in a rat model.
Methods: We used male Wistar rats. Animals in the intervention arm received a bolus of 50 U/kg of DA or saline injected into the tail vein after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration. We measured cytokine (tumour necrosis factor (TNF)alpha, interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-10) and HMGB1 levels in serum and lung tissue at regular intervals for 12 h following LPS injection. The mouse macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 was assessed following stimulation with LPS alone or concurrently with DA with identification of HMGB1 and other cytokines in the supernatant.
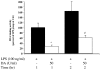
Results: Survival was significantly higher and lung histopathology significantly improved among the DA (50 U/kg) animals compared to the control rats. The serum and lung HMGB1 levels were lower over time among DA-treated animals. In the in vitro study, administration of DA was associated with decreased production of HMGB1. In the cell signalling studies, DA administration inhibited the phosphorylation of IkappaB.
Conclusion: DA decreases cytokine and HMGB1 levels during LPS-induced inflammation. As a result, DA ameliorated lung pathology and reduces mortality in endotoxin-induced systemic inflammation in a rat model. This effect may be mediated through the inhibition of cytokines and HMGB1.
Figures



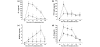



Similar articles
-
Danaparoid sodium prevents cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats.Shock. 2009 Jul;32(1):94-9. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31818ec2c2. Shock. 2009. PMID: 18948846
-
Danaparoid sodium attenuates the effects of heat stress.J Surg Res. 2011 Dec;171(2):762-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2010.05.008. Epub 2010 Jun 1. J Surg Res. 2011. PMID: 20673918
-
Danaparoid sodium attenuates the increase in inflammatory cytokines and preserves organ function in endotoxemic rats.Crit Care. 2008;12(4):R86. doi: 10.1186/cc6943. Epub 2008 Jul 6. Crit Care. 2008. PMID: 18601748 Free PMC article.
-
Ventilator-associated systemic inflammation in acute lung injury.Intensive Care Med. 2000 Oct;26(10):1411-3. doi: 10.1007/s001340000647. Intensive Care Med. 2000. PMID: 11126249 Review. No abstract available.
-
Nuclear factor-kappaB decoys suppress endotoxin-induced lung injury.Mol Pharmacol. 2005 Apr;67(4):977-9. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.011296. Epub 2005 Jan 26. Mol Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15673601 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Applicability of bedside ultrasonography for the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 and treatment with low molecular weight heparin.J Clin Ultrasound. 2020 Nov;48(9):522-526. doi: 10.1002/jcu.22898. Epub 2020 Aug 5. J Clin Ultrasound. 2020. PMID: 32757278 Free PMC article.
-
Progranulin deficiency leads to severe inflammation, lung injury and cell death in a mouse model of endotoxic shock.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Mar;20(3):506-17. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12756. Epub 2016 Jan 12. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26757107 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of HMGB1-targeting agents in sepsis.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008 Nov 4;10:e32. doi: 10.1017/S1462399408000884. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18980707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comment on Legrand et al.: The role of renal hypoperfusion in development of renal microcirculatory dysfunction in endotoxemic rats.Intensive Care Med. 2012 Feb;38(2):335; author reply 336. doi: 10.1007/s00134-011-2425-8. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Intensive Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22147113 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pharmacological Agents Targeting Thromboinflammation in COVID-19: Review and Implications for Future Research.Thromb Haemost. 2020 Jul;120(7):1004-1024. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1713152. Epub 2020 May 30. Thromb Haemost. 2020. PMID: 32473596 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM, Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, Manogue KR, Faist E, Abraham E, Andersson J, Andersson U, Molina PE, Abumrad NN, Sama A, Tracey KJ. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science. 1999;285:248–251. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5425.248. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

