Activation of olfactory and trigeminal cortical areas following stimulation of the nasal mucosa with low concentrations of S(-)-nicotine vapor--an fMRI study on chemosensory perception
- PMID: 18381635
- PMCID: PMC6870617
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20535
Activation of olfactory and trigeminal cortical areas following stimulation of the nasal mucosa with low concentrations of S(-)-nicotine vapor--an fMRI study on chemosensory perception
Abstract
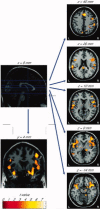
Applied to the nasal mucosa in low concentrations, nicotine vapor evokes odorous sensations (mediated by the olfactory system) whereas at higher concentrations nicotine vapor additionally produces burning and stinging sensations in the nose (mediated by the trigeminal system). The objective of this study was to determine whether intranasal stimulation with suprathreshold concentrations of S(-)-nicotine vapor causes brain activation in olfactory cortical areas or if trigeminal cortical areas are also activated. Individual olfactory detection thresholds for S(-)-nicotine were determined in 19 healthy occasional smokers using a computer-controlled air-dilution olfactometer. Functional magnetic resonance images were acquired using a 1.5T MR scanner with applications of nicotine in concentrations at or just above the individual's olfactory detection threshold. Subjects reliably perceived the stimuli as being odorous. Accordingly, activation of brain areas known to be involved in processing of olfactory stimuli was identified. Although most of the subjects never or only rarely observed a burning or painful sensation in the nose, brain areas associated with the processing of painful stimuli were activated in all subjects. This indicates that the olfactory and trigeminal systems are activated during perception of nicotine and it is not possible to completely separate olfactory from trigeminal effects by lowering the concentration of the applied nicotine. In conclusion, even at low concentrations that do not consistently lead to painful sensations, intranasally applied nicotine activates both the olfactory and the trigeminal system.
Figures


References
-
- Aceto MD,Martin BR ( 1982): Central actions of nicotine. Med Res Rev 2: 43–62. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht J,Wiesmann M ( 2006): The human olfactory system: Anatomy and physiology. Nervenarzt 77: 931–939. - PubMed
-
- Alimohammadi H,Silver WL. ( 2000): Evidence for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on nasal trigeminal nerve endings of the rat. Chem Senses 25: 61–66. - PubMed
-
- Anderson AK,Christoff K,Stappen I,Panitz D,Ghahremani DG,Glover G,Gabrieli JD,Sobel N ( 2003): Dissociated neural representations of intensity and valence in human olfaction. Nat Neurosci 6: 196–202. - PubMed
-
- Andersson JL,Hutton C,Ashburner J,Turner R,Friston K ( 2001): Modeling geometric deformations in EPI time series. Neuroimage 13: 903–919. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

