A synthetic Toll-like receptor 2 ligand decreases allergic immune responses in a mouse rhinitis model sensitized to mite allergen
- PMID: 18381801
- PMCID: PMC2276669
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B0730029
A synthetic Toll-like receptor 2 ligand decreases allergic immune responses in a mouse rhinitis model sensitized to mite allergen
Abstract
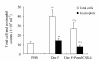
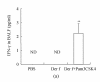
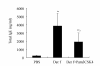
It has been proposed that activation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) plays crucial roles in the polarization of adaptive immune responses. A synthetic Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) ligand, Pam3CSK4, has been reported to modulate the balance of Th1/Th2 responses. We evaluated the modulation effect of Pam3CSK4 on allergic immune response in a mouse rhinitis model sensitized to house dust mite allergen (HDM). Mice were sensitized and challenged with Dermatophagoides farinae allergen (Der f), and then the allergic mice were treated by Pam3CSK4. Nasal allergic symptoms and eosinophils were scored. Der f-specific cytokine responses were examined in the splenocytes and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Serum level of total IgE was also detected. After establishing a mouse allergic rhinitis model with HDM, we have showed that Pam3CSK4 treatment not only ameliorated the nasal allergic symptoms remarkably but also decreased the eosinophils and total inflammation cells in BALF significantly. Analysis of cytokine profile found that IFN-gamma released from either BALF or stimulated splenocytes increased markedly in Pam3CSK4-treated mice, while IL-13 decreased significantly. Moreover, serum level of total IgE was significantly lower in Pam3CSK4-treated mice than in the untreated. Thus, in an allergic rhinitis mouse model developed with HDM, Pam3CSK4 was shown to exhibit an antiallergic effect, indicating its potential application in allergic diseases.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor 2 ligands inhibit TH2 responses to mite allergen.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006 May;117(5):1148-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2006.02.014. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16675345
-
Suppression of allergic response by CpG motif oligodeoxynucleotide-house-dust mite conjugate in animal model of allergic rhinitis.Am J Rhinol. 2006 Mar-Apr;20(2):212-8. Am J Rhinol. 2006. PMID: 16686392
-
[Immunotherapy with recombinant house dust mite group 2 allergen vaccine inhibits allergic airway inflammation in mice].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2006 Dec;24(6):414-9. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17366969 Chinese.
-
Attenuation of house dust mite Dermatophagoides farinae-induced airway allergic responses in mice by dehydroepiandrosterone is correlated with down-regulation of TH2 response.Clin Exp Allergy. 1999 Mar;29(3):414-22. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.00484.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999. PMID: 10202352
-
When the allergy alarm bells toll: The role of Toll-like receptors in allergic diseases and treatment.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jun 22;10:1204025. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1204025. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37426425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TLRs in pulmonary diseases.Life Sci. 2019 Sep 15;233:116671. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116671. Epub 2019 Jul 20. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31336122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DC priming by M. vaccae inhibits Th2 responses in contrast to specific TLR2 priming and is associated with selective activation of the CREB pathway.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 1;6(4):e18346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018346. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21483768 Free PMC article.
-
The Serine Protease Inhibitor, 4-(2-aminoethyl) Benzene Sulfonyl Fluoride Hydrochloride, Reduces Allergic Inflammation in a House Dust Mite Allergic Rhinitis Mouse Model.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014 Nov;6(6):558-66. doi: 10.4168/aair.2014.6.6.558. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 25374756 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 2 as a regulator of oral tolerance in the gastrointestinal tract.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:606383. doi: 10.1155/2014/606383. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 25309051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of allergic diseases and implications for therapeutic interventions.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Mar 24;8(1):138. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01344-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 36964157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agrawal S, Agrawal A, Doughty B, Gerwitz A, Blenis J, van Dyke T, Pulendran B. Cutting edge: different Toll-like receptor agonists instruct dendritic cells to induce distinct Th responses via differential modulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Fos. J Immunol. 2003;171(10):4984–4989. - PubMed
-
- Akdis CA, Kussebi F, Pulendran B, Akdis M, Lauener RP, Schmidt-Weber CB, Klunker S, Isitmangil G, Hansjee N, Wynn TA, et al. Inhibition of T helper 2-type responses, IgE production and eosinophilia by synthetic lipopeptides. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33(10):2717–2726. doi: 10.1002/eji.200323329. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akiba H, Mitsuishi K, Ikeda S, Okumura K, Ogawa H. Crucial commitment of proteolytic activity of a purified recombinant major house dust mite allergen Der p1 to sensitization toward IgE and IgG responses. J Immunol. 2006;177(3):1609–1617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

