The malate-aspartate NADH shuttle components are novel metabolic longevity regulators required for calorie restriction-mediated life span extension in yeast
- PMID: 18381895
- PMCID: PMC2279204
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1648308
The malate-aspartate NADH shuttle components are novel metabolic longevity regulators required for calorie restriction-mediated life span extension in yeast
Abstract
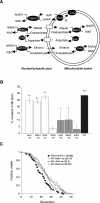
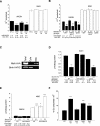
Recent studies suggest that increased mitochondrial metabolism and the concomitant decrease in NADH levels mediate calorie restriction (CR)-induced life span extension. The mitochondrial inner membrane is impermeable to NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, oxidized form) and NADH, and it is unclear how CR relays increased mitochondrial metabolism to multiple cellular pathways that reside in spatially distinct compartments. Here we show that the mitochondrial components of the malate-aspartate NADH shuttle (Mdh1 [malate dehydrogenase] and Aat1 [aspartate amino transferase]) and the glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle (Gut2, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) are novel longevity factors in the CR pathway in yeast. Overexpressing Mdh1, Aat1, and Gut2 extend life span and do not synergize with CR. Mdh1 and Aat1 overexpressions require both respiration and the Sir2 family to extend life span. The mdh1Deltaaat1Delta double mutation blocks CR-mediated life span extension and also prevents the characteristic decrease in the NADH levels in the cytosolic/nuclear pool, suggesting that the malate-aspartate shuttle plays a major role in the activation of the downstream targets of CR such as Sir2. Overexpression of the NADH shuttles may also extend life span by increasing the metabolic fitness of the cells. Together, these data suggest that CR may extend life span and ameliorate age-associated metabolic diseases by activating components of the NADH shuttles.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inborn disorders of the malate aspartate shuttle.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021 Jul;44(4):792-808. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12402. Epub 2021 May 24. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021. PMID: 33990986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced Ssy1-Ptr3-Ssy5 (SPS) signaling extends replicative life span by enhancing NAD+ homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 15;290(20):12753-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.644534. Epub 2015 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25825491 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogeny of malate-aspartate shuttle capacity and gene expression in cardiac mitochondria.Am J Physiol. 1998 Mar;274(3):C780-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1998.274.3.C780. Am J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9530110
-
The malate-aspartate shuttle (Borst cycle): How it started and developed into a major metabolic pathway.IUBMB Life. 2020 Nov;72(11):2241-2259. doi: 10.1002/iub.2367. Epub 2020 Sep 11. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 32916028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MDH1 deficiency is a metabolic disorder of the malate-aspartate shuttle associated with early onset severe encephalopathy.Hum Genet. 2019 Dec;138(11-12):1247-1257. doi: 10.1007/s00439-019-02063-z. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31538237
Cited by
-
The emergence of the nicotinamide riboside kinases in the regulation of NAD+ metabolism.J Mol Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 1;61(3):R107-R121. doi: 10.1530/JME-18-0085. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30307159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Effect of β-Lapachone and Aminooxyacetic Acid on Central Metabolism in Breast Cancer.Nutrients. 2022 Jul 22;14(15):3020. doi: 10.3390/nu14153020. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35893874 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide and Related Precursors as Therapeutic Targets for Age-Related Degenerative Diseases: Rationale, Biochemistry, Pharmacokinetics, and Outcomes.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019 Jan 10;30(2):251-294. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7269. Epub 2018 May 11. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019. PMID: 29634344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YCL047C/POF1 is a novel nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 30;289(22):15577-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.558643. Epub 2014 Apr 23. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24759102 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming and Host Tolerance: A Novel Concept to Understand Sepsis-Associated AKI.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 16;10(18):4184. doi: 10.3390/jcm10184184. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34575294 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aguilaniu H., Gustafsson L., Rigoulet M., Nystrom T. Asymmetric inheritance of oxidatively damaged proteins during cytokinesis. Science. 2003;299:1751–1753. - PubMed
-
- Albertyn J., Hohmann S., Thevelein J.M., Prior B.A. GPD1, which encodes glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, is essential for growth under osmotic stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and its expression is regulated by the high-osmolarity glycerol response pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994;14:4135–4144. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakker B.M., Overkamp K.M., van Maris A.J., Kotter P., Luttik M.A., van Dijken J.P., Pronk J.T. Stoichiometry and compartmentation of NADH metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2001;25:15–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
