Control of cell fate by the formation of an architecturally complex bacterial community
- PMID: 18381896
- PMCID: PMC2279205
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1645008
Control of cell fate by the formation of an architecturally complex bacterial community
Abstract
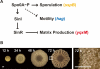
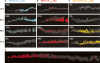
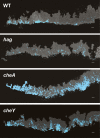
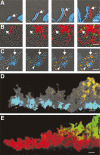
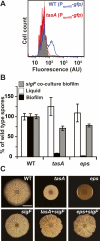
Bacteria form architecturally complex communities known as biofilms in which cells are held together by an extracellular matrix. Biofilms harbor multiple cell types, and it has been proposed that within biofilms individual cells follow different developmental pathways, resulting in heterogeneous populations. Here we demonstrate cellular differentiation within biofilms of the spore-forming bacterium Bacillus subtilis, and present evidence that formation of the biofilm governs differentiation. We show that motile, matrix-producing, and sporulating cells localize to distinct regions within the biofilm, and that the localization and percentage of each cell type is dynamic throughout development of the community. Importantly, mutants that do not produce extracellular matrix form unstructured biofilms that are deficient in sporulation. We propose that sporulation is a culminating feature of biofilm formation, and that spore formation is coupled to the formation of an architecturally complex community of cells.
Figures

References
-
- An D., Parsek M.R. The promise and peril of transcriptional profiling in biofilm communities. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007;10:292–296. - PubMed
-
- Branda S.S., Chu F., Kearns D.B., Losick R., Kolter R. A major protein component of the Bacillus subtilis biofilm matrix. Mol. Microbiol. 2006;59:1229–1238. - PubMed
-
- Burbulys D., Trach K.A., Hoch J.A. Initiation of sporulation in B. subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell. 1991;64:545–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
