The Young Men's Survey phase II: hepatitis B immunization and infection among young men who have sex with men
- PMID: 18382012
- PMCID: PMC2374826
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2006.101915
The Young Men's Survey phase II: hepatitis B immunization and infection among young men who have sex with men
Abstract
Objectives: We measured the prevalence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) immunization and HBV infection among men aged 23 to 29 years who have sex with men.
Methods: We analyzed data from 2834 men who have sex with men in 6 US metropolitan areas. Participants were interviewed and tested for serologic markers of immunization and HBV infection in 1998 through 2000.
Results: Immunization prevalence was 17.2%; coverage was 21.0% among participants with private physicians or health maintenance organizations and 12.6% among those with no source of health care. Overall, 20.6% had markers of HBV infection, ranging from 13.7% among the youngest to 31.0% among the oldest participants. Among those susceptible to HBV, 93.5% had regular sources of health care, had been tested for HIV, or had been treated for a sexually transmitted disease.
Conclusions: Although many young men who have sex with men have access to health care, most are not immunized against HBV. To reduce morbidity from HBV in this population, providers of health care, including sexually transmitted disease and HIV prevention services, should provide vaccinations or referrals for vaccination.
Figures
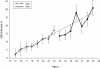
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Disease burden from Hepatitis A, B, and C in the United States. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/diseases/hepatitis/resource/PDFs/disease_burde.... Accessed June 27, 2006.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis Surveillance Report No. 59. Atlanta, Ga: US Dept of Health and Human Services; 2004.
-
- Blocker ME, Levine WC, St Louis ME. HIV prevalence in patients with syphilis, United States. Sex Transm Dis. 2000;27:53–59. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of syphilis among men who have sex with men—Southern California, 2000. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001;50(7):117–120. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines 2002. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2002;51(RR-6):1–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

