GABA(A) receptor trafficking and its role in the dynamic modulation of neuronal inhibition
- PMID: 18382465
- PMCID: PMC2709246
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn2370
GABA(A) receptor trafficking and its role in the dynamic modulation of neuronal inhibition
Abstract
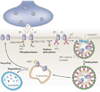
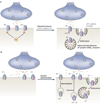
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) type A receptors (GABA(A)Rs) mediate most fast synaptic inhibition in the mammalian brain, controlling activity at both the network and the cellular levels. The diverse functions of GABA in the CNS are matched not just by the heterogeneity of GABA(A)Rs, but also by the complex trafficking mechanisms and protein-protein interactions that generate and maintain an appropriate receptor cell-surface localization. In this Review, we discuss recent progress in our understanding of the dynamic regulation of GABA(A)R composition, trafficking to and from the neuronal surface, and lateral movement of receptors between synaptic and extrasynaptic locations. Finally, we highlight a number of neurological disorders, including epilepsy and schizophrenia, in which alterations in GABA(A)R trafficking occur.
Figures


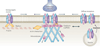
References
-
- Sieghart W, Sperk G. Subunit composition, distribution and function of GABAA receptor subtypes. Curr Top Med Chem. 2002;2:795–816. - PubMed
-
- Rudolph U, Mohler H. Analysis of GABAA receptor function and dissection of the pharmacology of benzodiazepines and general anesthetics through mouse genetics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:475–498. - PubMed
-
- Bormann J, Feigenspan A. GABAC receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1995;18:515–519. - PubMed
-
- Couve A, Moss SJ, Pangalos MN. GABAB receptors: a new paradigm in G protein signaling. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000;16:296–312. - PubMed
-
- Bettler B, Tiao JY. Molecular diversity, trafficking and subcellular localization of GABAB receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;110:533–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS056359/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048045/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS081986/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS048045/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS051195/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS051195/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 NS054900/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS046478/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 NS056359/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01NS054900/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047478/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS046478/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS080064/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

