Acute functional recovery of cerebral blood flow after forebrain ischemia in rat
- PMID: 18382471
- PMCID: PMC2771551
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2008.21
Acute functional recovery of cerebral blood flow after forebrain ischemia in rat
Abstract
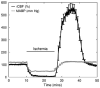
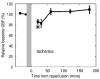
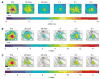
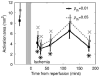
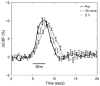
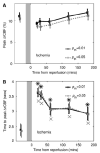
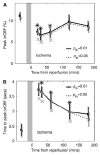
After complete cerebral ischemia, the postischemic blood flow response to functional activation is severely attenuated for several hours. However, little is known about the spatial and temporal extent of the blood flow response in the acute postischemic period after incomplete cerebral ischemia. To investigate the relative cerebral blood flow (rCBF) response in the somatosensory cortex of rat to controlled vibrissae stimulation after transient incomplete ischemia (15-min bilateral common carotid artery occlusion+hypotension), we employed laser speckle imaging combined with statistical parametric mapping. We found that the ischemic insult had a significant impact on the baseline blood flow (P<0.005) and the activation area in response to functional stimulation was significantly reduced after ischemia (P<0.005). The maximum rCBF response in the activation area determined from the statistical analysis did not change significantly up to 3 h after ischemia (P>0.1). However, the time when rCBF response reached its maximum was significantly delayed (P<0.0001) from 2.4+/-0.2 secs before ischemia to 3.6+/-0.1 secs at 20 mins into reperfusion (P<0.001); the delay was reduced gradually to 2.9+/-0.2 secs after 3 h, which was still significantly greater than that observed before the insult (P=0.04).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of pentoxifylline on cerebral blood flow, metabolism, and evoked response after total cerebral ischemia in dogs.Crit Care Med. 1994 Feb;22(2):273-81. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199402000-00019. Crit Care Med. 1994. PMID: 8306687
-
Effects of clentiazem on cerebral ischemia induced by carotid artery occlusion in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats.Stroke. 1994 Feb;25(2):474-80. doi: 10.1161/01.str.25.2.474. Stroke. 1994. PMID: 8303759
-
Regional glucose utilization and blood flow following graded forebrain ischemia in the rat: correlation with neuropathology.Ann Neurol. 1985 Oct;18(4):470-81. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180410. Ann Neurol. 1985. PMID: 4073840
-
Changes in Cerebral Blood Flow in the Postischemic Period.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2016 Mar;160(5):610-3. doi: 10.1007/s10517-016-3229-1. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27021103
-
[Neurofunctional disturbances as related to cortical ischemia and white matter ischemia].No To Shinkei. 1989 Feb;41(2):117-24. No To Shinkei. 1989. PMID: 2736142 Japanese.
Cited by
-
Expanding applications, accuracy, and interpretation of laser speckle contrast imaging of cerebral blood flow.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015 Jul;35(7):1076-84. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.84. Epub 2015 May 6. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015. PMID: 25944593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extraction of tissue optical property and blood flow from speckle contrast diffuse correlation tomography (scDCT) measurements.Biomed Opt Express. 2021 Sep 1;12(9):5894-5908. doi: 10.1364/BOE.429890. eCollection 2021 Sep 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 34692223 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive noncontact speckle contrast diffuse correlation tomography of cerebral blood flow in rats.Neuroimage. 2019 Sep;198:160-169. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.05.047. Epub 2019 May 18. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 31112789 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of image exposure time into a modified laser speckle imaging method.Phys Med Biol. 2010 Nov 21;55(22):6857-66. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/22/016. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Phys Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 21048287 Free PMC article.
-
Calibration of diffuse correlation spectroscopy with a time-resolved near-infrared technique to yield absolute cerebral blood flow measurements.Biomed Opt Express. 2011 Jul 1;2(7):2068-81. doi: 10.1364/BOE.2.002068. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Biomed Opt Express. 2011. PMID: 21750781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ances BM, Greenberg JH, Detre JA. Acute carotid occlusion alters the activation flow coupling response to forepaw stimulation in a rat model. Stroke. 2000;31:955–60. - PubMed
-
- Ances BM, Wilson DF, Greenberg JH, Detre JA. Dynamic changes in cerebral blood flow, O2 tension, and calculated cerebral metabolic rate of O2 during functional activation using oxygen phosphorescence quenching. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21:511–6. - PubMed
-
- Ayata C, Dunn AK, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Huang ZH, Boas DA, Moskowitz MA. Laser speckle flowmetry for the study of cerebrovascular physiology in normal and ischemic mouse cortex. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004;24:744–55. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay R, Gittings AS, Suh SS, Dixon PK, Durian DJ. Speckle-visibility spectroscopy: a tool to study time-varying dynamics. Rev Sci Instru. 2005;76:093110.
-
- Benzi G, Dagani F, Arrigoni E. Acute model for the estimation of the cerebral energy state during or after hypoxia and complete or incomplete ischaemia. Eur Neurol. 1978;17:87–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

