Effects of radix adenophorae and cyclosporine A on an OVA-induced murine model of asthma by suppressing to T cells activity, eosinophilia, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness
- PMID: 18382613
- PMCID: PMC2276601
- DOI: 10.1155/2008/781425
Effects of radix adenophorae and cyclosporine A on an OVA-induced murine model of asthma by suppressing to T cells activity, eosinophilia, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness
Abstract
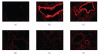
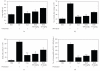
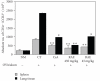
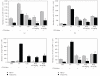
The present study is performed to investigate the inhibitory effects of Radix Adenophorae extract (RAE) on ovalbumin-induced asthma murine model. To study the anti-inflammatory and antiasthmatic effects of RAE, we examined the development of pulmonary eosinophilic inflammation and inhibitory effects of T cells in murine by RAE and cyclosporine A (CsA). We examined determination of airway hyperresponsiveness, flow cytometric analysis (FACS), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), quantitative real time (PCR), hematoxylin-eosin staining, and Masson trichrome staining in lung tissue, lung weight, total cells, and eosinophil numbers in lung tissue. We demonstrated how RAE suppressed development on inflammation and decreased airway damage.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effects of Actinidia polygama extract and cyclosporine A on OVA-induced eosinophilia and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of asthma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2006 Apr;6(4):703-13. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2005.10.007. Epub 2005 Nov 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16504935
-
Fritillaria cirrhosa, Anemarrhena asphodeloides, Lee-Mo-Tang and cyclosporine a inhibit ovalbumin-induced eosinophil accumulation and Th2-mediated bronchial hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of asthma.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007 Mar;100(3):205-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2007.00043.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17309526
-
Curcumin attenuates allergic airway inflammation by regulation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells (Tregs)/Th17 balance in ovalbumin-sensitized mice.Fitoterapia. 2013 Jun;87:57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2013.02.014. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Fitoterapia. 2013. PMID: 23500387
-
Immunostimulatory DNA mediates inhibition of eosinophilic inflammation and airway hyperreactivity independent of natural killer cells in vivo.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001 Nov;108(5):759-63. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.118795. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11692101
-
Effects of post-inhalation treatment with interleukin-12 on airway hyper-reactivity, eosinophilia and interleukin-18 receptor expression in a mouse model of asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2002 Apr;32(4):641-9. doi: 10.1046/j.0954-7894.2002.01346.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002. PMID: 11972614
Cited by
-
Adenophora Stricta Root Extract Protects Lung Injury from Exposure to Particulate Matter 2.5 in Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 15;11(7):1376. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071376. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883867 Free PMC article.
-
A cell-impermeable cyclosporine A derivative reduces pathology in a mouse model of allergic lung inflammation.J Immunol. 2010 Dec 15;185(12):7663-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001707. Epub 2010 Nov 5. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21057089 Free PMC article.
-
Antiasthmatic effects of hesperidin, a potential Th2 cytokine antagonist, in a mouse model of allergic asthma.Mediators Inflamm. 2011;2011:485402. doi: 10.1155/2011/485402. Epub 2011 May 4. Mediators Inflamm. 2011. PMID: 21772663 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of anti-asthmatic potential of dried fruits of Vitis vinifera L. in animal model of bronchial asthma.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2016 Aug 17;12:42. doi: 10.1186/s13223-016-0145-x. eCollection 2016. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27536321 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of Chinese herbal medicine as an adjunctive therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057604. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jun ZG. Collection of Illustrative Plates for Identification and Application on Clinical Traditional Chinese Drug. Beijing, China: Renminweishengchubanshe; 2002.
-
- Xiaopeigen . Modern Chinese Material Medica. Beijing, China: Huaxuegongyechubanshe; 2002.
-
- Akihisa T, Yasukawa K, Yamaura M, et al. Triterpene alcohol and sterol ferulates from rice bran and their anti-inflammatory effects. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2000;48(6):2313–2319. - PubMed
-
- Akihisa T, Yasukawa K, Oinuma H, et al. Triterpene alcohols from the flowers of compositae and their anti-inflammatory effects. Phytochemistry. 1996;43(6):1255–1260. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

