DJ-1 modulates alpha-synuclein aggregation state in a cellular model of oxidative stress: relevance for Parkinson's disease and involvement of HSP70
- PMID: 18382667
- PMCID: PMC2270347
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001884
DJ-1 modulates alpha-synuclein aggregation state in a cellular model of oxidative stress: relevance for Parkinson's disease and involvement of HSP70
Retraction in
-
Retraction: DJ-1 Modulates α-Synuclein Aggregation State in a Cellular Model of Oxidative Stress: Relevance for Parkinson's Disease and Involvement of HSP70.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 24;15(1):e0219023. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219023. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31978049 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative pathology whose molecular etiopathogenesis is not known. Novel contributions have come from familial forms of PD caused by alterations in genes with apparently unrelated physiological functions. The gene coding for alpha-synuclein (alpha-syn) (PARK1) has been investigated as alpha-syn is located in Lewy bodies (LB), intraneuronal inclusions in the substantia nigra (SN) of PD patients. A-syn has neuroprotective chaperone-like and antioxidant functions and is involved in dopamine storage and release. DJ-1 (PARK7), another family-PD-linked gene causing an autosomal recessive form of the pathology, shows antioxidant and chaperone-like activities too.
Methodology/principal findings: The present study addressed the question whether alpha-syn and DJ-1 interact functionally, with a view to finding some mechanism linking DJ-1 inactivation and alpha-syn aggregation and toxicity. We developed an in vitro model of alpha-syn toxicity in the human neuroblastoma cell line SK-N-BE, influencing DJ-1 and alpha-syn intracellular concentrations by exogenous addition of the fusion proteins TAT-alpha-syn and TAT-DJ-1; DJ-1 was inactivated by the siRNA method. On a micromolar scale TAT-alpha-syn aggregated and triggered neurotoxicity, while on the nanomolar scale it was neuroprotective against oxidative stress (induced by H(2)O(2) or 6-hydroxydopamine). TAT-DJ-1 increased the expression of HSP70, while DJ-1 silencing made SK-N-BE cells more susceptible to oxidative challenge, rendering TAT-alpha-syn neurotoxic at nanomolar scale, with the appearance of TAT-alpha-syn aggregates.
Conclusion/significance: DJ-1 inactivation may thus promote alpha-syn aggregation and the related toxicity, and in this model HSP70 is involved in the antioxidant response and in the regulation of alpha-syn fibril formation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
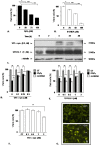
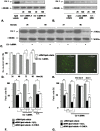
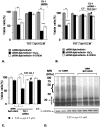
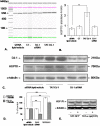

Similar articles
-
The Parkinson's disease-related protein DJ-1 protects dopaminergic neurons in vivo and cultured cells from alpha-synuclein and 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity.Neurodegener Dis. 2015;15(1):13-23. doi: 10.1159/000367993. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Neurodegener Dis. 2015. PMID: 25500798
-
The deglycase activity of DJ-1 mitigates α-synuclein glycation and aggregation in dopaminergic cells: Role of oxidative stress mediated downregulation of DJ-1 in Parkinson's disease.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 May 1;135:28-37. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.02.014. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30796974
-
Protective effect of TAT-delivered alpha-synuclein: relevance of the C-terminal domain and involvement of HSP70.FASEB J. 2004 Nov;18(14):1713-5. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-1621fje. Epub 2004 Sep 2. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 15345691
-
[Alpha-synuclein interacted proteins: the relevance with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2008 Sep;37(5):524-30. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2008.05.019. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2008. PMID: 18925724 Review. Chinese.
-
Reprint of: revisiting oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease-resemblance to the effect of amphetamine drugs of abuse.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Sep;62:186-201. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.042. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23743292 Review.
Cited by
-
BAG1 restores formation of functional DJ-1 L166P dimers and DJ-1 chaperone activity.J Cell Biol. 2010 Feb 22;188(4):505-13. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200904103. Epub 2010 Feb 15. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20156966 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in genetic animal models of Parkinson's disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 May 1;16(9):896-919. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4200. Epub 2011 Oct 4. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 21848447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Physical Interaction between the Dopamine Transporter and DJ-1 Facilitates Increased Dopamine Reuptake.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 25;10(8):e0136641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136641. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26305376 Free PMC article.
-
α-synuclein expression from a single copy transgene increases sensitivity to stress and accelerates neuronal loss in genetic models of Parkinson's disease.Exp Neurol. 2018 Dec;310:58-69. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Exp Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30194957 Free PMC article.
-
Rifampicin reduces alpha-synuclein in a transgenic mouse model of multiple system atrophy.Neuroreport. 2008 Aug 27;19(13):1271-6. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32830b3661. Neuroreport. 2008. PMID: 18695506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Di Monte DA. The environment and Parkinson's disease: is the nigrostriatal system preferentially targeted by neurotoxins? Lancet Neurol. 2003;2:531–538. - PubMed
-
- Fahn S. Description of Parkinson's disease as a clinical syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;991:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J, Cookson MR, Singleton A. Genes and parkinsonism. Lancet Neurol. 2003;2:221–228. - PubMed
-
- Gosal D, Ross OA, Toft M. Parkinson's disease: the genetics of a heterogeneous disorder. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13:616–627. - PubMed
-
- Klein C, Schlossmacher MG. The genetics of Parkinson disease: Implications for neurological care. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2006;2:136–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

