p27 deficiency cooperates with Bcl-2 but not Bax to promote T-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 18382684
- PMCID: PMC2270898
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001911
p27 deficiency cooperates with Bcl-2 but not Bax to promote T-cell lymphoma
Abstract
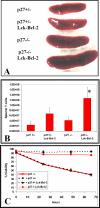
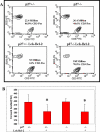
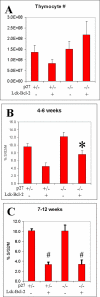
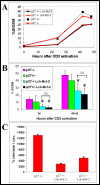
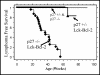
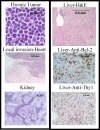
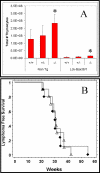
The effect of Bcl-2 on oncogenesis is complex and expression may either delay or accelerate oncogenesis. The pro-oncogenic activity is attributed to its well characterized anti-apoptotic function while the anti-oncogenic function has been attributed to its inhibition of cellular proliferation. Recent studies demonstrate that p27 may mediate the effects of Bcl-2 on cellular proliferation. We hypothesized that p27 may suppress tumor formation by Bcl-2 family members. To test this hypothesis, cell cycle inhibition and lymphoma development were examined in Lck-Bcl-2 and Lck-Bax38/1 transgenic mice deficient in p27. Strikingly, p27 deficiency synergistically cooperates with Bcl-2 to increase T cell hyperplasia and development of spontaneous T cell lymphomas. Within 1 year, >90% of these mice had developed thymic T cell lymphomas. This high penetrance contrasts with a one year incidence of <5% of thymic lymphoma in Lck-Bcl-2 or p27 -/- mice alone. In contrast, p27 deficiency had no effect on tumor formation in Lck-Bax38/1 transgenic mice, another model of T cell lymphoma. Histologically the lymphomas in p27 -/- Lck-Bcl-2 mice are lymphoblastic and frequently involve multiple organs suggesting an aggressive phenotype. Interestingly, in mature splenic T cells, Bcl-2 largely retains its anti-proliferative function even in the absence of p27. T cells from p27 -/- Lck-Bcl-2 mice show delayed kinetics of CDK2 Thr-160 phosphorylation. This delay is associated with a delay in the up regulation of both Cyclin D2 and D3. These data demonstrate a complex relationship between the Bcl-2 family, cellular proliferation, and oncogenesis and demonstrate that p27 up-regulation is not singularly important in the proliferative delay observed in T cells expressing Bcl-2 family members. Nonetheless, the results indicate that p27 is a critical tumor suppressor in the context of Bcl-2 expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
BCL-x(L) and BCL2 delay Myc-induced cell cycle entry through elevation of p27 and inhibition of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases.Oncogene. 2002 Nov 7;21(51):7765-75. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205928. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12420213
-
Bax accelerates tumorigenesis in p53-deficient mice.Cancer Res. 2001 Jan 15;61(2):659-65. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11212265
-
Silencing Bcl-2 in models of mantle cell lymphoma is associated with decreases in cyclin D1, nuclear factor-kappaB, p53, bax, and p27 levels.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Apr;7(4):749-58. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0302. Epub 2008 Mar 28. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18375822
-
Expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1) in AIDS-related diffuse large-cell lymphomas is associated with Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1.Am J Pathol. 2002 Jul;161(1):163-71. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64168-5. Am J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12107101 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphoma development in Bax transgenic mice is inhibited by Bcl-2 and associated with chromosomal instability.Cell Death Differ. 2003 Jun;10(6):740-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401233. Cell Death Differ. 2003. PMID: 12761582
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs and Glucocorticoid-Induced Apoptosis in Lymphoid Malignancies.ISRN Hematol. 2013;2013:348212. doi: 10.1155/2013/348212. Epub 2013 Jan 29. ISRN Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23431463 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase inhibition blocks cell death and enhances mitophagy but fails to promote T-cell lymphoma.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e19786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019786. Epub 2011 May 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21611191 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Effect of Fluoxetine and Sertraline on Chronic Stress-Induced Tumor Growth and Cell Dissemination in a Mouse Model of Lymphoma: Crucial Role of Antitumor Immunity.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 19;9:1341. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01341. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29971064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakhshi A, Jensen JP, Goldman P, Wright JJ, McBride OW, et al. Cloning the chromosomal breakpoint of t(14;18) human lymphomas: clustering around JH on chromosome 14 and near a transcriptional unit on 18. Cell. 1985;41:899–906. - PubMed
-
- Tsujimoto Y, Gorham J, Cossman J, Jaffe E, Croce CM. The t(14:18) chromosome translocations involved in B-cell neoplasms result from mistakes in VDJ joining. Science. 1985;229:1390–1393. - PubMed
-
- Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ. BCL-2 Family -Regulators of Cell Death. Annual Review of Immunology. 1998;16:395–419. - PubMed
-
- Kuwana T, Newmeyer DD. Bcl-2-family proteins and the role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2003;15:691–699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

