Toll-like receptor ligands induce human T cell activation and death, a model for HIV pathogenesis
- PMID: 18382686
- PMCID: PMC2271052
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001915
Toll-like receptor ligands induce human T cell activation and death, a model for HIV pathogenesis
Abstract
Background: Recently, heightened systemic translocation of microbial products was found in persons with chronic HIV infection and this was linked to immune activation and CD4(+) T cell homeostasis.
Methodology: We examined here the effects of microbial Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands on T cell activation in vitro.
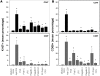
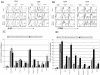
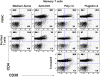
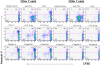
Conclusions/findings: We show that exposure to TLR ligands results in activation of memory and effector CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells. After exposure to each of 8 different ligands that activate TLRs 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, and 9, CD8(+) T cells are activated and gain expression of the C type lectin CD69 that may promote their retention in lymphoid tissues. In contrast, CD4(+) T cells rarely increase CD69 expression but instead enter cell cycle. Despite activation and cell cycle entry, CD4(+) T cells divide poorly and instead, disproportionately undergo activation-induced cell death. Systemic exposure to TLR agonists may therefore increase immune activation, effector cell sequestration in lymphoid tissues and T cell turnover. These events may contribute to the pathogenesis of immune dysfunction and CD4+ T cell losses in chronic infection with the human immunodeficiency virus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
HIV-induced type I interferon and tryptophan catabolism drive T cell dysfunction despite phenotypic activation.PLoS One. 2008 Aug 13;3(8):e2961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002961. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18698365 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of CD80, CD86 and CD70 on T cells from HIV-infected individuals upon activation in vitro: regulation by CD4+ T cells.Eur J Immunol. 1996 Aug;26(8):1700-6. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260806. Eur J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8765009
-
A Novel Toll-Like Receptor 9 Agonist, MGN1703, Enhances HIV-1 Transcription and NK Cell-Mediated Inhibition of HIV-1-Infected Autologous CD4+ T Cells.J Virol. 2016 Apr 14;90(9):4441-4453. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00222-16. Print 2016 May. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26889036 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle dysregulation during HIV infection: perspectives of a target based therapy.Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2002 Apr;2(1):53-61. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2002. PMID: 12477296 Review.
-
Emerging Role and Characterization of Immunometabolism: Relevance to HIV Pathogenesis, Serious Non-AIDS Events, and a Cure.J Immunol. 2016 Jun 1;196(11):4437-44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600120. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27207806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human β defensin-3 induces chemokines from monocytes and macrophages: diminished activity in cells from HIV-infected persons.Immunology. 2013 Dec;140(4):413-20. doi: 10.1111/imm.12148. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23829433 Free PMC article.
-
Learning from the messengers: innate sensing of viruses and cytokine regulation of immunity - clues for treatments and vaccines.Viruses. 2013 Jan 31;5(2):470-527. doi: 10.3390/v5020470. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23435233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tuftsin promotes an anti-inflammatory switch and attenuates symptoms in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34933. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034933. Epub 2012 Apr 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22529957 Free PMC article.
-
TLR9 polymorphism correlates with immune activation, CD4 decline and plasma IP10 levels in HIV patients.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Jan 16;19(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-3697-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30651082 Free PMC article.
-
Human labour is associated with altered regulatory T cell function and maternal immune activation.Clin Exp Immunol. 2020 Feb;199(2):182-200. doi: 10.1111/cei.13384. Epub 2019 Nov 3. Clin Exp Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31617583 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Hornung V, Rothenfusser S, Britsch S, Krug A, Jahrdorfer B, et al. Quantitative expression of toll-like receptor 1-10 mRNA in cellular subsets of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and sensitivity to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. J Immunol. 2002;168:4531–7. - PubMed
-
- Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:987–95. - PubMed
-
- Brenchley JM, Price DA, Schacker TW, Asher TE, Silvestri G, et al. Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat Med. 2006;12 (12):1365–71. - PubMed
-
- Silvestri G, Sodora DL, Koup RA, Paiardini M, O'Neil SP, et al. Nonpathogenic SIV infection of sooty mangabeys is characterized by limited bystander immunopathology despite chronic high-level viremia. Immunity. 2003;18:441–52. - PubMed
-
- Sancho D, Gomez M, Sanchez-Madrid F. CD69 is an immunoregulatory molecule induced following activation. Trends Immunol. 2005;26:136–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

