Estrogen receptor and breast MR imaging features: a correlation study
- PMID: 18383260
- PMCID: PMC2613434
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.21330
Estrogen receptor and breast MR imaging features: a correlation study
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the MRI features between estrogen receptor (ER) positive and negative breast cancers.
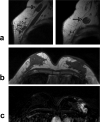
Materials and methods: Breast MRI of 90 consecutive patients confirmed with invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), 51 ER positive and 39 ER negative, were analyzed. The tumor morphology and dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) kinetics were evaluated based on the American College of Radiology (ACR) Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) MRI lexicon and compared. Enlarged axillary lymph nodes on MRI and choline (Cho) detection using MR spectroscopy (MRS) were also analyzed and compared. For patients receiving axillary node dissection the pathological nodal status was also compared.
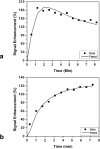
Results: ER negative breast cancer had bigger tumors compared to ER positive cancer (3.6 +/- 2.0 cm vs. 1.8 +/- 1.3 cm, P < 0.00005). ER negative cancer was more likely to exhibit nonmass type enhancements compared to ER positive cancer (P < 0.005). Enlarged axillary lymph nodes were more frequently identified on MRI in ER negative compared to ER positive patients (P < 0.05). After excluding patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy, auxiliary lymph node status did not show significant difference between ER positive and ER negative cancer on MRI and pathology. ER negative cancer was more likely to show the malignant type enhancement kinetics (P = 0.15), rim enhancement (P = 0.15), and Cho detection on MRS (P = 0.23) compared to ER positive cancer, but it did not reach a level of statistical significance.
Conclusion: ER negative breast cancer was more aggressive, with larger tumor size, more non-mass-type enhancement lesions, and a higher percentage showing enlarged axillary nodes on MRI. These features might be related to its poorer cellular differentiation and/or a higher angiogenesis.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
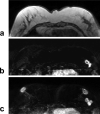
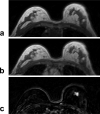
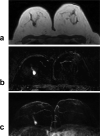
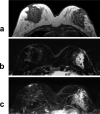


References
-
- Yasui Y, Potter JD. The shape of age-incidence curves of female breast cancer by hormone-receptor status. Cancer Causes Control. 1999;10:431–437. - PubMed
-
- Bernoux A, de Cremoux P, Lainé-Bidron C, Martin EC, Asselain B, Magdelénat H. Estrogen receptor negative and progesterone receptor positive primary breast cancer: pathological characteristics and clinical outcome. Institut Curie Breast Cancer Study Group. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998;49:219–225. - PubMed
-
- Putti TC, El-Rehim DM, Rakha EA, et al. Estrogen receptor-negative breast carcinomas: a review of morphology and immunophenotypical analysis. Mod Pathol. 2005;18:26–35. - PubMed
-
- Sanna G, Franceschelli L, Rotmensz N, et al. Brain metastases in patients with advanced breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:2865–2869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

