Neuronal pigmented autophagic vacuoles: lipofuscin, neuromelanin, and ceroid as macroautophagic responses during aging and disease
- PMID: 18384642
- PMCID: PMC6609458
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05385.x
Neuronal pigmented autophagic vacuoles: lipofuscin, neuromelanin, and ceroid as macroautophagic responses during aging and disease
Abstract
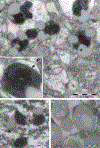
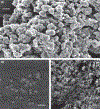
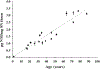
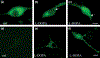
The most striking morphologic change in neurons during normal aging is the accumulation of autophagic vacuoles filled with lipofuscin or neuromelanin pigments. These organelles are similar to those containing the ceroid pigments associated with neurologic disorders, particularly in diseases caused by lysosomal dysfunction. The pigments arise from incompletely degraded proteins and lipids principally derived from the breakdown of mitochondria or products of oxidized catecholamines. Pigmented autophagic vacuoles may eventually occupy a major portion of the neuronal cell body volume because of resistance of the pigments to lysosomal degradation and/or inadequate fusion of the vacuoles with lysosomes. Although the formation of autophagic vacuoles via macroautophagy protects the neuron from cellular stress, accumulation of pigmented autophagic vacuoles may eventually interfere with normal degradative pathways and endocytic/secretory tasks such as appropriate response to growth factors.
Figures
References
-
- Adamec E, Mohan PS, Cataldo AM, Vonsattel JP and Nixon RA (2000) Up-regulation of the lysosomal system in experimental models of neuronal injury: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience, 100, 663–675. - PubMed
-
- Anglade P, Vyas S, Javoy-Agid F et al. (1997) Apoptosis and auto-phagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Histol. Histopathol, 12, 25–31. - PubMed
-
- Assuncao M, de Freitas V and Paula-Barbosa M (2007) Grape seed flavanols, but not Port wine, prevent ethanol-induced neuronal lipofuscin formation. Brain Res, 1129, 72–80. - PubMed
-
- Bampton ET, Goemans CG, Niranjan D, Mizushima N and Tolkovsky AM (2005) The dynamics of autophagy visualized in live cells: from autophagosome formation to fusion with endo/lysosomes. Autophagy, 1, 23–36. - PubMed
-
- Barden H (1970) Relationship of golgi thiaminepyrosphosphatase and lysosomal acid phosphatase to neuromelanin and lipofuscin in cerebral neurons of the aging rhesus monkey. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol, 29, 225–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

