Presynaptic calcium channel localization and calcium-dependent synaptic vesicle exocytosis regulated by the Fuseless protein
- PMID: 18385325
- PMCID: PMC2769928
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5553-07.2008
Presynaptic calcium channel localization and calcium-dependent synaptic vesicle exocytosis regulated by the Fuseless protein
Abstract
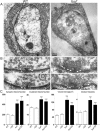
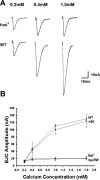
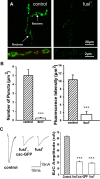
A systematic forward genetic Drosophila screen for electroretinogram mutants lacking synaptic transients identified the fuseless (fusl) gene, which encodes a predicted eight-pass transmembrane protein in the presynaptic membrane. Null fusl mutants display >75% reduction in evoked synaptic transmission but, conversely, an approximately threefold increase in the frequency and amplitude of spontaneous synaptic vesicle fusion events. These neurotransmission defects are rescued by a wild-type fusl transgene targeted only to the presynaptic cell, demonstrating a strictly presynaptic requirement for Fusl function. Defects in FM dye turnover at the synapse show a severely impaired exo-endo synaptic vesicle cycling pool. Consistently, ultrastructural analyses reveal accumulated vesicles arrested in clustered and docked pools at presynaptic active zones. In the absence of Fusl, calcium-dependent neurotransmitter release is dramatically compromised and there is little enhancement of synaptic efficacy with elevated external Ca(2+) concentrations. These defects are causally linked with severe loss of the Cacophony voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels, which fail to localize normally at presynaptic active zone domains in the absence of Fusl. These data indicate that Fusl regulates assembly of the presynaptic active zone Ca(2+) channel domains required for efficient coupling of the Ca(2+) influx and synaptic vesicle exocytosis during neurotransmission.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ceramidase regulates synaptic vesicle exocytosis and trafficking.J Neurosci. 2004 Sep 8;24(36):7789-803. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1146-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15356190 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in a Drosophila alpha2delta voltage-gated calcium channel subunit reveal a crucial synaptic function.J Neurosci. 2008 Jan 2;28(1):31-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4498-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18171920 Free PMC article.
-
Separation of presynaptic Cav2 and Cav1 channel function in synaptic vesicle exo- and endocytosis by the membrane anchored Ca2+ pump PMCA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jul 13;118(28):e2106621118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2106621118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34244444 Free PMC article.
-
Exocytosis and endocytosis of synaptic vesicles and functional roles of vesicle pools: lessons from the Drosophila neuromuscular junction.Neuroscientist. 2005 Apr;11(2):138-47. doi: 10.1177/1073858404271679. Neuroscientist. 2005. PMID: 15746382 Review.
-
Physical link and functional coupling of presynaptic calcium channels and the synaptic vesicle docking/fusion machinery.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1998 Aug;30(4):335-45. doi: 10.1023/a:1021985521748. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1998. PMID: 9758330 Review.
Cited by
-
The nonsense-mediated decay pathway maintains synapse architecture and synaptic vesicle cycle efficacy.J Cell Sci. 2010 Oct 1;123(Pt 19):3303-15. doi: 10.1242/jcs.069468. Epub 2010 Sep 7. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20826458 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic CaV2 calcium channel traffic requires CALF-1 and the alpha(2)delta subunit UNC-36.Nat Neurosci. 2009 Oct;12(10):1257-65. doi: 10.1038/nn.2383. Epub 2009 Aug 30. Nat Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19718034 Free PMC article.
-
Loose coupling between calcium channels and sites of exocytosis in chromaffin cells.J Physiol. 2009 Nov 15;587(Pt 22):5377-91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.176065. Epub 2009 Sep 14. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19752110 Free PMC article.
-
N-glycosylation requirements in neuromuscular synaptogenesis.Development. 2013 Dec;140(24):4970-81. doi: 10.1242/dev.099192. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Development. 2013. PMID: 24227656 Free PMC article.
-
FM Dye Cycling at the Synapse: Comparing High Potassium Depolarization, Electrical and Channelrhodopsin Stimulation.J Vis Exp. 2018 May 24;(135):57765. doi: 10.3791/57765. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 29889207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambudkar IS. TRPC1: a core component of store-operated calcium channels. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35:96–100. - PubMed
-
- Andrews HK, Zhang YQ, Trotta N, Broadie K. Drosophila sec10 is required for hormone secretion but not general exocytosis or neurotransmission. Traffic. 2002;3:906–921. - PubMed
-
- Aravamudan B, Broadie K. Synaptic Drosophila UNC-13 is regulated by antagonistic G-protein pathways via a proteasome-dependent degradation mechanism. J Neurobiol. 2003;54:417–438. - PubMed
-
- Aravamudan B, Fergestad T, Davis WS, Rodesch CK, Broadie K. Drosophila UNC-13 is essential for synaptic transmission. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:965–971. - PubMed
-
- Becherer U, Moser T, Stuhmer W, Oheim M. Calcium regulates exocytosis at the level of single vesicles. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:846–853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
