Detecting evolutionary relationships across existing fold space, using sequence order-independent profile-profile alignments
- PMID: 18385384
- PMCID: PMC2291117
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0704422105
Detecting evolutionary relationships across existing fold space, using sequence order-independent profile-profile alignments
Abstract
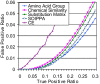
Here, a scalable, accurate, reliable, and robust protein functional site comparison algorithm is presented. The key components of the algorithm consist of a reduced representation of the protein structure and a sequence order-independent profile-profile alignment (SOIPPA). We show that SOIPPA is able to detect distant evolutionary relationships in cases where both a global sequence and structure relationship remains obscure. Results suggest evolutionary relationships across several previously evolutionary distinct protein structure superfamilies. SOIPPA, along with an increased coverage of protein fold space afforded by the structural genomics initiative, can be used to further test the notion that fold space is continuous rather than discrete.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: This work is part of a provisional patent application filed by the University of California San Diego (University of California San Diego Reference No. SD2008-001-1).
Figures



References
-
- Orengo CA, Thornton JM. Protein families and their evolution—a structural perspective. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:867–900. - PubMed
-
- Whisstock JC, Lesk AM. Prediction of protein function from protein sequence and structure. Q Rev Biophys. 2003;36:307–340. - PubMed
-
- Dobson PD, Cai YD, Stapley BJ, Doig AJ. Prediction of protein function in the absence of significant sequence similarity. Curr Med Chem. 2004;11:2135–2142. - PubMed
-
- Andreeva A, Murzin AG. Evolution of protein fold in the presence of functional constraints. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006;16:399–408. - PubMed
-
- Murzin AG. How far divergent evolution goes in protein. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998;8:380–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

