Src inhibition ameliorates polycystic kidney disease
- PMID: 18385429
- PMCID: PMC2440293
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2007060665
Src inhibition ameliorates polycystic kidney disease
Abstract
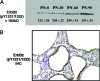
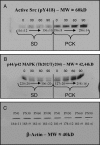
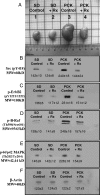
Despite identification of the genes responsible for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (PKD) and autosomal recessive PKD (ARPKD), the precise functions of their cystoprotein products remain unknown. Recent data suggested that multimeric cystoprotein complexes initiate aberrant signaling cascades in PKD, and common components of these signaling pathways may be therapeutic targets. This study identified c-Src (pp60(c-Src)) as one such common signaling intermediate and sought to determine whether Src activity plays a role in cyst formation. With the use of the nonorthologous BPK murine model and the orthologous PCK rat model of ARPKD, greater Src activity was found to correlate with disease progression. Inhibition of Src activity with the pharmacologic inhibitor SKI-606 resulted in amelioration of renal cyst formation and biliary ductal abnormalities in both models. Furthermore, the effects of Src inhibition in PCK kidneys suggest that the ErbB2 and B-Raf/MEK/ERK pathways are involved in Src-mediated signaling in ARPKD and that this occurs without reducing elevated cAMP. These data suggest that Src inhibition may provide therapeutic benefit in PKD.
Figures






References
-
- Ong AC, Harris PC: Molecular pathogenesis of ADPKD: The polycystin complex gets complex. Kidney Int 67: 1234–1247, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Ward CJ, Hogan MC, Rossetti S, Walker D, Sneddon T, Wang X, Kubly V, Cunningham JM, Bacallao R, Ishibashi M, Milliner DS, Torres VE, Harris PC: The gene mutated in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease encodes a large, receptor-like protein. Nat Genet 30: 259–269, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Onuchic LF, Furu L, Nagasawa Y, Hou X, Eggermann T, Ren Z, Bergmann C, Senderek J, Esquivel E, Zeltner R, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Mrug M, Sweeney W, Avner ED, Zerres K, Guay-Woodford LM, Somlo S, Germino GG: PKHD1, the polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 gene, encodes a novel large protein containing multiple immunoglobulin-like plexin-transcription-factor domains and parallel beta-helix 1 repeats. Am J Hum Genet 70: 1305–1317, 2002 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dell K, McDonald R, Watkins SL, Avner ED: Polycystic kidney disease. In: Pediatric Nephrology, 5th Ed., edited by Avner ED, Harmon WE, Niaudet P, Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2004, pp 675–699
-
- Pazour GJ, San Agustin JT, Follit JA, Rosenbaum JL, Witman GB: Polycystin-2 localizes to kidney cilia and the ciliary level is elevated in orpk mice with polycystic kidney disease. Curr Biol 12: R378–R380, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

