Identification of thermotolerant campylobacter species by fluorescence in situ hybridization
- PMID: 18385439
- PMCID: PMC2446828
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01512-07
Identification of thermotolerant campylobacter species by fluorescence in situ hybridization
Abstract
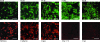
Thermotolerant Campylobacter spp. (Campylobacter jejuni, C. coli, C. lari, and C. upsaliensis) are leading causes of food-borne diarrhea in humans. In this study, the usefulness of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) for the identification of Campylobacter isolates was investigated. A hierarchical FISH probe set that included six group-, genus-, and species-specific probes was developed and evaluated with 12 reference strains and 94 clinical isolates of Campylobacter, Arcobacter, and Helicobacter. FISH correctly identified all isolates to the genus level and detected all thermotolerant Campylobacter isolates. The assay showed high degrees of sensitivity for the identification of C. jejuni (90%), C. coli (97%), C. lari (81%), and C. upsaliensis (100%) to the species level.
Figures
References
-
- Barros-Velazquez, J., A. Jimenez, and T. G. Villa. 1999. Isolation and typing methods for the epidemiologic investigation of thermotolerant campylobacters. Int. Microbiol. 2217-226. - PubMed
-
- Chan, V., G. Crocetti, M. Grehan, L. Zhang, S. Danon, A. Lee, and H. Mitchell. 2005. Visualization of Helicobacter species within the murine cecal mucosa using specific fluorescence in situ hybridization. Helicobacter 10114-124. - PubMed
-
- Diergaardt, S. M., S. N. Venter, A. Spreeth, J. Theron, and V. S. Brozel. 2004. The occurrence of campylobacters in water sources in South Africa. Water Res. 382589-2595. - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald, C., and I. Nachamkin. 2007. Campylobacter and Arcobacter, p. 933-946. In P. R. Murray, E. J. Baron, J. H. Jorgensen, M. L. Landry, and M. A. Pfaller (ed.), Manual of clinical microbiology, 9th ed. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

