Comparison of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid a protein in septic shock patients
- PMID: 18385816
- PMCID: PMC2277077
- DOI: 10.1155/2008/631414
Comparison of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid a protein in septic shock patients
Abstract
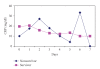
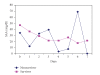
Septic shock is a severe inflammatory state caused by an infectious agent. Our purpose was to investigate serum amyloid A (SAA) protein and C-reactive protein (CRP) as inflammatory markers of septic shock patients. Here we evaluate 29 patients in postoperative period, with septic shock, in a prospective study developed in a surgical intensive care unit. All eligible patients were monitored over a 7-day period by sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score, daily CRP, SAA, and lactate measurements. CRP and SAA strongly correlated up to the fifth day of observation but were not good predictors of mortality in septic shock.
Figures
References
-
- Luzzani A, Polati E, Dorizzi R, Rungatscher A, Pavan R, Merlini A. Comparison of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as markers of sepsis. Critical Care Medicine. 2003;31(6):1737–1741. - PubMed
-
- Enguix A, Rey C, Concha A, Medina A, Coto D, Diéguez MA. Comparison of procalcitonin with C-reactive protein and serum amyloid for the early diagnosis of bacterial sepsis in critically ill neonates and children. Intensive Care Medicine. 2001;27(1):211–215. - PubMed
-
- Patel H, Fellowes R, Coade S, Woo P. Human serum amyloid A has cytokine-like properties. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology. 1998;48(4):410–418. - PubMed
-
- Gabay C, Kushner I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. New England Journal of Medicine. 1999;340(6):448–454. - PubMed
-
- Urieli-Shoval S, Linke RP, Matzner Y. Expression and function of serum amyloid A, a major acute-phase protein, in normal and disease states. Current Opinion in Hematology. 2000;7(1):64–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous