Alterations of RB1 gene in embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: special reference to utility of pRB immunoreactivity in differential diagnosis of rhabdomyosarcoma subtype
- PMID: 18386058
- PMCID: PMC12161760
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-008-0385-3
Alterations of RB1 gene in embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: special reference to utility of pRB immunoreactivity in differential diagnosis of rhabdomyosarcoma subtype
Abstract
Purpose: Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), which is the most common pediatric soft tissue sarcoma, is classified into two major histologic subtypes, embryonal RMS (ERMS) and alveolar RMS (ARMS). RMS is occasionally reported to be the second neoplasm of hereditary retinoblastoma. Osteosarcoma is known as the most common second neoplasm of hereditary retinoblastoma, and tumorigenesis of osteosarcoma has been proven in previous studies to be related to the RB gene (RB1) alteration. Therefore, there might be a correlation between the tumorigenesis of RMS and RB1 alteration.
Methods: We examined the RB protein (pRB) expression and RB1 alteration such as allelic imbalance (gain or loss) and homozygous deletion, using immunohistochemistry, microsatellite makers, and quantitative real-time PCR in 57 sporadic RMS.
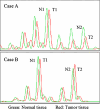
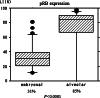
Results: Allelic imbalance was more frequently detected in ERMS (13/27), than in ARMS (3/20) (P = 0.04). Homozygous deletion on the protein-binding pocket domain of RB1 was found in 6 of 27 ERMS and in 2 of 20 ARMS (P = 0.24). Furthermore, immunohistochemical pRB labeling indexes (LI) in 31 ERMS (median value, 31%) were significantly reduced in comparison with those observed in 26 ARMS (median value, 85%) (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Our results support the assertion that tumorigenesis of RMS may be associated with RB1 alteration especially in ERMS, as previously reported for osteosarcoma. As for the RB pathway, each subtype of RMS may have a different tumorigenesis. In addition, immunohistochemical pRB LI may have the potential to be a useful ancillary tool in the differential diagnosis of RMS subtypes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
FGFR1 fusions as a novel molecular driver in rhabdomyosarcoma.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2024 Apr;63(4):e23232. doi: 10.1002/gcc.23232. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38607246 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation is a key regulator of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) cell viability and migration.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Jun;145(6):1461-1469. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02913-3. Epub 2019 Apr 21. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31006845 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can a Liquid Biopsy Detect Circulating Tumor DNA With Low-passage Whole-genome Sequencing in Patients With a Sarcoma? A Pilot Evaluation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jan 1;483(1):39-48. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003161. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 38905450
-
Fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) computed tomography (CT) for the detection of bone, lung, and lymph node metastases in rhabdomyosarcoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 9;11(11):CD012325. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012325.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34753195 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic deregulation of microRNAs in rhabdomyosarcoma and neuroblastoma and translational perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Dec 5;13(12):16554-79. doi: 10.3390/ijms131216554. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23443118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoregulatory loop between TGF-β1/miR-411-5p/SPRY4 and MAPK pathway in rhabdomyosarcoma modulates proliferation and differentiation.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Aug 20;6(8):e1859. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.225. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26291313 Free PMC article.
-
NFκB signaling in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.Dis Model Mech. 2017 Sep 1;10(9):1109-1115. doi: 10.1242/dmm.030882. Dis Model Mech. 2017. PMID: 28883017 Free PMC article.
-
Myogenetic Oligodeoxynucleotides as Anti-Nucleolin Aptamers Inhibit the Growth of Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 25;10(11):2691. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112691. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359210 Free PMC article.
-
Soft tissue sarcomas with non-EWS translocations: molecular genetic features and pathologic and clinical correlations.Virchows Arch. 2010 Feb;456(2):153-66. doi: 10.1007/s00428-009-0776-0. Epub 2009 Apr 28. Virchows Arch. 2010. PMID: 19396640 Review.
References
-
- Aerts I, Pacquement H, Doz F, Mosseri V, Desjardins L, Sastre X, Michon J, Rodriguez J, Schlienger P, Zucker JM, Quintana E (2004) Outcome of second malignancies after retinoblastoma: a retrospective analysis of 25 patients treated at the Institut Curie. Eur J Cancer 40:1522–1529 - PubMed
-
- Asakura A, Rudnicki MA (2003) Rhabdomyosarcomagenesis-Novel pathway found. Cancer Cell 4:421–422 - PubMed
-
- Berggren P, Kumar R, Sakano S, Hemminki L, Wada T, Steineck G, Adolfsson J, Larsson P, Norming U, Wijkstrom H, Hemminki K (2003) Detecting homozygous deletions in the CDKN2A(p16(INK4a))/ARF(p14(ARF)) gene in urinary bladder cancer using real-time quantitative PCR. Clin Cancer Res 9:235–242 - PubMed
-
- Bergthorsson JT, Agnarsson BA, Gudbjartsson T, Magnusson K, Thoroddsen A, Palsson B, Bjornsson J, Stefansson K, Gulcher J, Einarsson GV, Amundadottir LT, Barkardottir RB (2006) A genome-wide study of allelic imbalance in human testicular germ cell tumors using microsatellite markers. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 164:1–9 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

