Mutations to Ku reveal differences in human somatic cell lines
- PMID: 18387344
- PMCID: PMC2427147
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.02.008
Mutations to Ku reveal differences in human somatic cell lines
Abstract
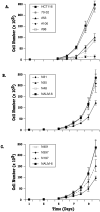
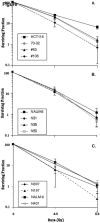
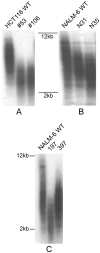
NHEJ (non-homologous end joining) is the predominant mechanism for repairing DNA double-stranded breaks in human cells. One essential NHEJ factor is the Ku heterodimer, which is composed of Ku70 and Ku86. Here we have generated heterozygous loss-of-function mutations for each of these genes in two different human somatic cell lines, HCT116 and NALM-6, using gene targeting. Previous work had suggested that phenotypic differences might exist between the genes and/or between the cell lines. By providing a side-by-each comparison of the four cell lines, we demonstrate that there are indeed subtle differences between loss-of-function mutations for Ku70 versus Ku86, which is accentuated by whether the mutations were derived in the HCT116 or NALM-6 genetic background. Overall, however, the phenotypes of the four lines are quite similar and they provide a compelling argument for the hypothesis that Ku loss-of-function mutations in human somatic cells result in demonstrable haploinsufficiencies. Collectively, these studies demonstrate the importance of proper biallelic expression of these genes for NHEJ and telomere maintenance and they provide insights into why these genes are uniquely essential for primates.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Heterozygous inactivation of human Ku70/Ku86 heterodimer does not affect cell growth, double-strand break repair, or genome integrity.DNA Repair (Amst). 2006 Mar 7;5(3):303-11. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2005.10.008. Epub 2005 Dec 1. DNA Repair (Amst). 2006. PMID: 16325483
-
Ku86 represses lethal telomere deletion events in human somatic cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jul 28;106(30):12430-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903362106. Epub 2009 Jul 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19581589 Free PMC article.
-
Human LIGIV is synthetically lethal with the loss of Rad54B-dependent recombination and is required for certain chromosome fusion events induced by telomere dysfunction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Feb 1;41(3):1734-49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1326. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23275564 Free PMC article.
-
The Ku heterodimer: function in DNA repair and beyond.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2015 Jan-Mar;763:15-29. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jul 4. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2015. PMID: 25795113 Review.
-
Ku, a DNA repair protein with multiple cellular functions?Mutat Res. 1999 May 14;434(1):3-15. doi: 10.1016/s0921-8777(99)00006-3. Mutat Res. 1999. PMID: 10377944 Review.
Cited by
-
High-efficiency targeted transgene integration via primed micro-homologues.Cell Discov. 2023 Jul 4;9(1):69. doi: 10.1038/s41421-023-00552-0. Cell Discov. 2023. PMID: 37402729 Free PMC article.
-
Long telomeres bypass the requirement for telomere maintenance in human tumorigenesis.Cell Rep. 2012 Feb 23;1(2):91-8. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2011.12.004. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 22832159 Free PMC article.
-
A DNA-PKcs mutation in a radiosensitive T-B- SCID patient inhibits Artemis activation and nonhomologous end-joining.J Clin Invest. 2009 Jan;119(1):91-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI37141. Epub 2008 Dec 15. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19075392 Free PMC article.
-
ATM, ATR and DNA-PKcs kinases-the lessons from the mouse models: inhibition ≠ deletion.Cell Biosci. 2020 Jan 29;10:8. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-0376-x. eCollection 2020. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32015826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PRKDC mutations in a SCID patient with profound neurological abnormalities.J Clin Invest. 2013 Jul;123(7):2969-80. doi: 10.1172/JCI67349. Epub 2013 Jun 3. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23722905 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maser RS, DePinho RA. Connecting chromosomes, crisis, and cancer. Science. 2002;297:565–569. - PubMed
-
- Hefferin ML, Tomkinson AE. Mechanism of DNA double-strand break repair by non-homologous end joining. DNA Repair. 2005;4:639–648. - PubMed
-
- Jung D, Alt FW. Unraveling V(D)J recombination. Insights into gene regulation. Cell. 2004;116:299–311. - PubMed
-
- Meek K, Gupta S, Ramsden DA, Lees-Miller SP. The DNA-dependent protein kinase: the director at the end. Immunol. Rev. 2004;200:132–141. - PubMed
-
- Cahill D, Connor B, Carney JP. Mechanisms of eukaryotic DNA double strand break repair. Front Biosci. 2006;11:1958–1976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

