Mutation that dramatically alters rat titin isoform expression and cardiomyocyte passive tension
- PMID: 18387630
- PMCID: PMC2501117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.02.272
Mutation that dramatically alters rat titin isoform expression and cardiomyocyte passive tension
Abstract
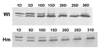
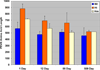
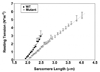
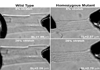
Titin is a very large alternatively spliced protein that performs multiple functions in heart and skeletal muscles. A rat strain is described with an autosomal dominant mutation that alters the isoform expression of titin. While wild type animals go through a developmental program where the 3.0 MDa N2B becomes the major isoform expressed by two to three weeks after birth (approximately 85%), the appearance of the N2B is markedly delayed in heterozygotes and never reaches more than 50% of the titin in the adult. Homozygote mutants express a giant titin of the N2BA isoform type (3.9 MDa) that persists as the primary titin species through ages of more than one and a half years. The mutation does not affect the isoform switching of troponin T, a protein that is also alternatively spliced with developmental changes. The basis for the apparently greater size of the giant titin in homozygous mutants was not determined, but the additional length was not due to inclusion of sequence from larger numbers of PEVK exons or the Novex III exon. Passive tension measurements using isolated cardiomyocytes from homozygous mutants showed that cells could be stretched to sarcomere lengths greater than 4 mum without breakage. This novel rat model should be useful for exploring the potential role of titin in the Frank-Starling relationship and mechano-sensing/signaling mechanisms.
Figures




Comment in
-
Some rat: a very special rat with a rather special titin.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008 Jun;44(6):976-978. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.03.017. Epub 2008 Apr 1. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18455183 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Maruyama K. Connectin, an elastic protein from myofibrils. J Biochem (Tokyo) 1976;80:405–407. - PubMed
-
- Granzier HL, Labeit S. Titin and its associated proteins: the third myofilament system of the sarcomere. Adv Protein Chem. 2005;71:89–119. - PubMed
-
- Granzier H, Wu Y, Siegfried L, LeWinter M. Titin: physiological function and role in cardiomyopathy and failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2005;10:211–223. - PubMed
-
- LeWinter MM, Wu Y, Labeit S, Granzier H. Cardiac titin: structure, functions and role in disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2007;375:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

