To (TGF)beta or not to (TGF)beta: fine-tuning of Smad signaling via post-translational modifications
- PMID: 18387785
- PMCID: PMC2597537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.02.003
To (TGF)beta or not to (TGF)beta: fine-tuning of Smad signaling via post-translational modifications
Abstract
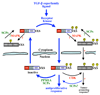
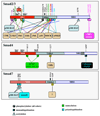
Smad proteins are key signal transducers for the TGF-beta superfamily and are frequently inactivated in human cancers, yet the molecular basis of how their levels and activities are regulated remains unclear. Recent progress, discussed herein, illustrates the critical roles of Smad post-translational modifications in the cellular outcome to TGF-beta signaling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of TGF-β Family Signaling by Inhibitory Smads.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017 Mar 1;9(3):a022095. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022095. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017. PMID: 27920040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β Signaling from Receptors to Smads.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016 Sep 1;8(9):a022061. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022061. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016. PMID: 27449815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β-activated kinase 1 (Tak1) mediates agonist-induced Smad activation and linker region phosphorylation in embryonic craniofacial neural crest-derived cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 10;288(19):13467-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.431775. Epub 2013 Apr 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23546880 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the quantitative nature of TGF-beta/Smad signaling.Trends Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;18(9):430-42. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.06.006. Epub 2008 Aug 15. Trends Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18706811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-translational regulation of TGF-β receptor and Smad signaling.FEBS Lett. 2012 Jul 4;586(14):1871-84. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.010. Epub 2012 May 19. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22617150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transforming growth factor-(beta)s and mammary gland involution; functional roles and implications for cancer progression.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2009 Jun;14(2):131-44. doi: 10.1007/s10911-009-9122-z. Epub 2009 Apr 25. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2009. PMID: 19396528 Free PMC article.
-
OSR1 phosphorylates the Smad2/3 linker region and induces TGF-β1 autocrine to promote EMT and metastasis in breast cancer.Oncogene. 2021 Jan;40(1):68-84. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01499-2. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33051597
-
SIRT2 alleviated renal fibrosis by deacetylating SMAD2 and SMAD3 in renal tubular epithelial cells.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Sep 30;14(9):646. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06169-1. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37777567 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of USP15, TβR-I and Smad7 in psoriasis.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2014 Jun;34(3):415-419. doi: 10.1007/s11596-014-1293-1. Epub 2014 Jun 18. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24939309
-
Regulation of Krüppel-like factor 4 by the anaphase promoting complex pathway is involved in TGF-beta signaling.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 4;286(9):6890-901. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.179952. Epub 2010 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21177849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whitman M, Raftery L. Development. 2005;132:4205–4210. - PubMed
-
- Akhurst RJ. Nat Genet. 2004;36:790–792. - PubMed
-
- Blobe GC, Schiemann WP, Lodish HF. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1350–1358. - PubMed
-
- Massague J, Blain SW, Lo RS. Cell. 2000;103:295–309. - PubMed
-
- Waite KA, Eng C. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4:763–773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

