An essential ligand-binding domain in the membrane receptor for retinol-binding protein revealed by large-scale mutagenesis and a human polymorphism
- PMID: 18387951
- PMCID: PMC2397481
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M801060200
An essential ligand-binding domain in the membrane receptor for retinol-binding protein revealed by large-scale mutagenesis and a human polymorphism
Abstract
Plasma retinol-binding protein (RBP), the principal carrier of vitamin A in the blood, delivers vitamin A from liver, the site of storage, to distant organs that need vitamin A, such as the eye, brain, placenta, and testis. STRA6 is a high-affinity membrane receptor for RBP and mediates vitamin A uptake in these target organs. STRA6 is a 74-kDa multi-transmembrane domain protein that represents a new class of membrane transport protein. In this study, we used an unbiased strategy by analyzing >900 random mutants of STRA6 to study its structure and function, and we identified an essential RBP-binding domain in STRA6. Mutations in any of the three essential residues in this domain can almost completely abolish binding of STRA6 to RBP and its vitamin A uptake activity from holo-RBP without affecting its cell surface expression. We have also functionally characterized the mutations in human STRA6 that cause severe birth defects as well as several human polymorphisms. All STRA6 mutants associated with severe birth defects have largely abolished vitamin A uptake activity, consistent with the severe clinical phenotypes. In addition, we have identified a human polymorphism that significantly reduces the vitamin A uptake activity of STRA6. Interestingly, the residue affected by this polymorphism is located in the RBP-binding domain we identified, and the polymorphism causes decreased vitamin A uptake by reducing RBP binding. This study identifies an essential functional domain in STRA6 and a human polymorphism in this domain that leads to reduced vitamin A uptake activity.
Figures


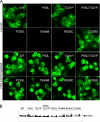
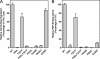
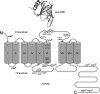
Similar articles
-
Regulatory mechanism for the transmembrane receptor that mediates bidirectional vitamin A transport.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 May 5;117(18):9857-9864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1918540117. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32300017 Free PMC article.
-
The membrane receptor for plasma retinol-binding protein, a new type of cell-surface receptor.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2011;288:1-41. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386041-5.00001-7. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21482409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-time analyses of retinol transport by the membrane receptor of plasma retinol binding protein.J Vis Exp. 2013 Jan 28;(71):e50169. doi: 10.3791/50169. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 23407361 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin A Transport and Cell Signaling by the Retinol-Binding Protein Receptor STRA6.Subcell Biochem. 2016;81:77-93. doi: 10.1007/978-94-024-0945-1_3. Subcell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27830501 Review.
-
The STRA6 receptor is essential for retinol-binding protein-induced insulin resistance but not for maintaining vitamin A homeostasis in tissues other than the eye.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 23;288(34):24528-39. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.484014. Epub 2013 Jul 9. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23839944 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Techniques to study specific cell-surface receptor-mediated cellular vitamin A uptake.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;652:341-61. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-325-1_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20552439 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic architecture of retinoic-acid signaling-associated ocular developmental defects.Hum Genet. 2019 Sep;138(8-9):937-955. doi: 10.1007/s00439-019-02052-2. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31359131 Review.
-
Loss of the systemic vitamin A transporter RBPR2 affects the quantitative balance between chromophore and opsins in visual pigment synthesis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 11:2024.07.08.602543. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.08.602543. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: FASEB J. 2025 Mar 15;39(5):e70407. doi: 10.1096/fj.202403090R. PMID: 39026765 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
STRA6-catalyzed vitamin A influx, efflux, and exchange.J Membr Biol. 2012 Nov;245(11):731-45. doi: 10.1007/s00232-012-9463-1. Epub 2012 Jul 20. J Membr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22815070 Free PMC article.
-
Retina, retinol, retinal and the natural history of vitamin A as a light sensor.Nutrients. 2012 Dec 19;4(12):2069-96. doi: 10.3390/nu4122069. Nutrients. 2012. PMID: 23363998 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goodman, D. S. (1984) in The Retinoids (Sporn, M. B., Boberts, A. B., and Goodman, D. S., eds) pp. 41-88, Academic Press, Orlando, FL
-
- Newcomer, M. E., and Ong, D. E. (2000) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1482 57-64 - PubMed
-
- Blaner, W. S. (1989) Endocr. Rev. 10 308-316 - PubMed
-
- Zanotti, G., and Berni, R. (2004) Vitam. Horm. 69 271-295 - PubMed
-
- Bok, D., and Heller, J. (1976) Exp. Eye Res. 22 395-402 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

